Landschlacht, Switzerland, 30 December 2017
In this season of goodwill and gratitude for all the blessings we enjoy, those who are healthy should especially be thankful, for we live in an age when life expectancy is higher because mankind has developed medicines and methods to extend life and restore health.

Granted there is still much significant progress needed, for far too many people still fall victim to the scourges of cancer and strokes.
There is still much we do not understand about diseases like Parkinson´s, AIDS and far too many others to comprehensively list here.
Even the common cold with its endless variety of mutations remains unsolvable and must simply be accepted as one of the countless burdens we must endure in life.

What is significant about today when compared with yesteryear is that common injuries are less likely to be fatal.
As well through the contributions of thoughtful compassionate innovators, our attitudes towards the care of the injured and ailing have improved.
Here in Switzerland and back in my homeland of Canada I have been hospitalized due to injuries caused by accidents: a fall from a tree (shattered shoulder), an axe slip (shattered foot), and a fall on a staircase (shattered wrist).
And though I also have medical conditions of anemia and celiac, neither these conditions nor the accidents I have had led to risks of fatality.
For prompt and compassionate medical attention provided to me ensured that I still live a functional, mostly painless, and happy healthy existence.
For the Christian West, Christmas is the season to show thanksgiving to God for sending His Son Jesus Christ to save our immortal souls, we also should not forget the human instruments of change that have assisted mankind to save our mortal flesh.

I married a doctor, and, even though she is a children´s physician, knowing her has given me an appreciation of just how difficult a profession medicine really is at all levels of medical treatment.
From the surgeon whose precision must be matched with efficiency, to the specialist doctor whose diagnosis must be accurately matched with the most likely cause of the patient´s symptoms, to the technicians who operate machinery that can reveal the interior of a patient´s body, to the family doctor who must know when to send a patient to a specialist and when to trust his/her own treatment, to the pharmacist that must know what medicines do and how to administer them, to the administrator who must balance the needs of patients with the cost of maintaining those needs, to the cleaning staff who ensure that the health care environment is as sterile as humanly possible, to the therapist who teaches the patient how to heal him/herself, to the nurse who monitors and comforts the bedbound sick person unable to fend for him/herself…..
The world of health care is a complex and complicated system demanding dedicated people and a neverending desire to improve itself.
A visit to a London museum two months ago has made me consider how grateful I am that an Englishwoman had the courage to be compassionate, Christian, and transformed the world for the better.

London, England, 24 October 2017
As mentioned in great detail in my blogpost Canada Slim and the Royal Peculiar my wife and I visited Westminster Abbey, that necrophiliac fetish house for the Establishment.
And folks whether or not they were avowed antiestablishment found themselves commemorated here.
The poet Shelley, despite wishing to be known as an anarchist artist and was buried in Rome, is memorialised here in Poets´ Corner, across from Viscount Castlereagh, a man Shelley loathed.

Above: Percy Bysshe Shelley (1792 – 1822)
“I met Murder on the way.

Above: Robert Stewart, Viscount Castlereagh (1769 – 1822)
He had a face like Castlereagh.”
Before leaving the Abbey, we briefly visited the Undercroft Museum with its death-worshipping collection of royal funeral effigies.
Until the Middle Ages, British monarchs were traditionally embalmed and left to lie in state for a set period of time.
Eventually, the corpse was substituted for a wooden figure of the deceased, fully dressed with clothes from the Great Wardrobe and displayed on top of the funeral carriage for the final journey.
As the clothes were expected to fit the effegy perfectly, the likenesses found in the Undercroft are probably fairly accurate.
Edward III´s face has a strange leer, a recreation of the stroke he suffered in his final years.

Above: Westminster Abbey effigy of Edward III (1312 – 1377)
His eyebrows came from a plucked dog.
Several soldiers are known as the Ragged Regiment due to their decrepit decay.
Frances, the Duchess of Richmond and Lennox, holds what may be the world´s oldest stuffed bird, an African Grey parrot that died in 1702.

Above: Frances Teresa Stewart (1647 – 1702)
Samuel Pepys wrote in his diary that Frances was the greatest beauty he had ever seen.
Sadly she was disfigured by smallpox in 1668.
Sadly her final fate no different than that of her parrot.
Leaving the Abbey we see the Methodist Central Hall, an inadequate and unnecessary replacement to the building that once stood here.
On this site once stood the Royal Aquarium and Winter Garden, opened in 1876, a grand Victorian entertainment venue.

It housed palm trees, restaurants, an art gallery, an orchestra, a skating rink, the Imperial Theatre, smoking and reading rooms.
A variety of sea creatures were displayed here, but the Aquarium was often plagued by frequent plumbing problems, so the place became better known for the exciting performances staged here than for the fish.
Come one, come all.
See William Leonard Hunt, aka the Great Farini, the world renowned Canadian showman and tightrope walker!
Above: William Hunt, aka the Great Farini (1838 – 1929)
Gasp in awe at 14-year-old Rossa Matilda Richter, aka Zazel, the first ever human cannonball, as she (barely 5 feet tall and 64 lbs heavy) is launched through the air flying 30 feet or more!
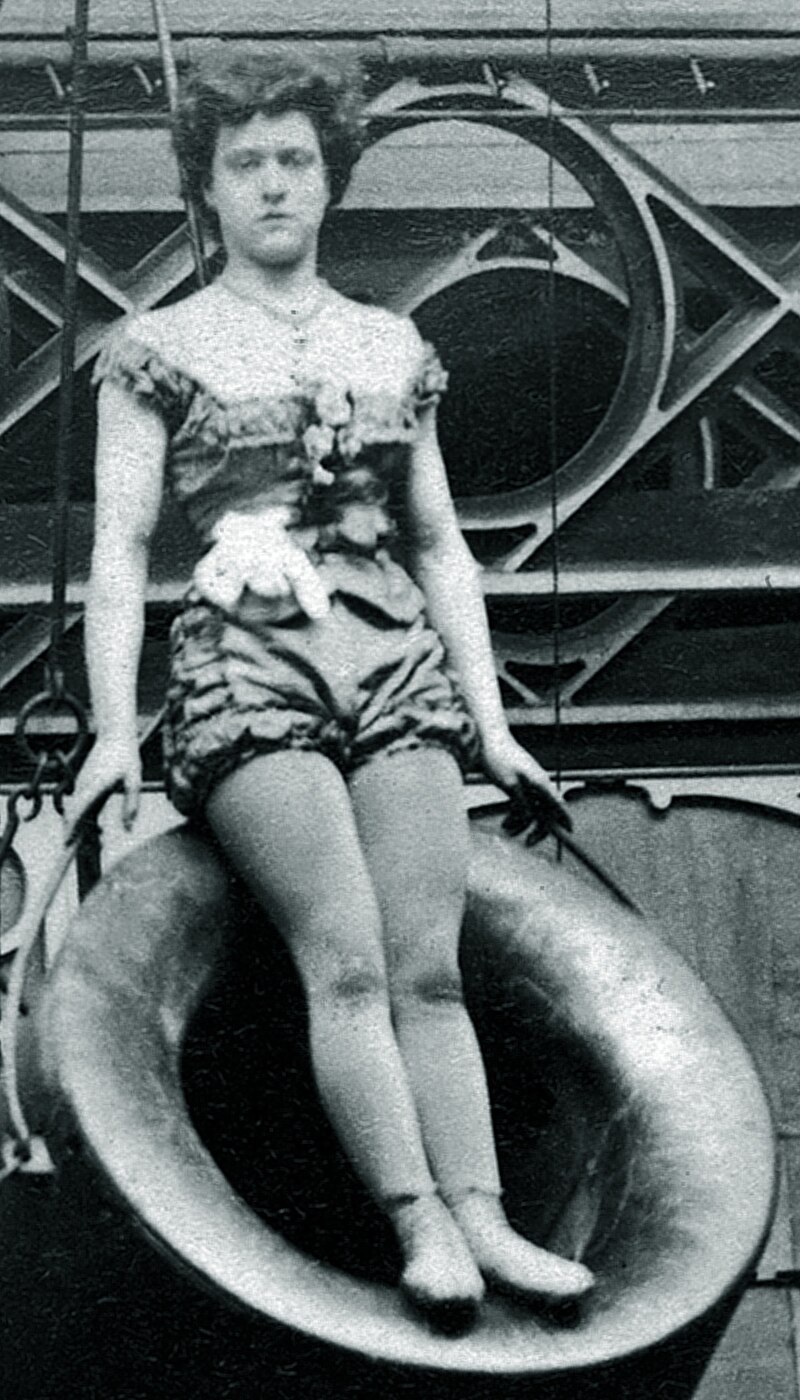

Above: Rossa Richter, aka Zazel (1863 – 1929)
Protests were launched over the danger Zazel faced and for a while the venue was in danger of losing its license but crowds kept coming to see the performances.

By the 1890s the Aquarium´s reputation became disreputable and it became known as a place where ladies of poor character went in search of male companions.
The Great Farini and Zazel were one thing, but an Aquarium of ill repute was too much for Victorian propriety to accept.
The Aquarium closed in 1899 and was demolished four years later.
In 1905 construction began on the Hall for Methodists, Christianity´s least entertaining sect.
We headed towards the Thames and followed Millbank Road to a place which suffered the opposite fate of the Aquarium.
While the Aquarium lost its aura of entertainment and was replaced by a stodgy religious institute, opposite the Tate Britain Museum is an almost invisible plaque upon an unremarkable bollard that tells the reader that where the entertaining Tate stands once stood Millbank Prison.

Above: Tate Britain
Millbank was built to serve as the National Petientiary and was used as a holding facility for convicts due for transportation to Australia.

“Near this site stood Millbank Prison which was opened in 1816 and closed in 1890.
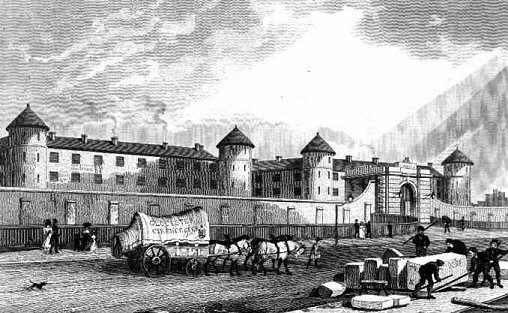
This buttress stood at the head of the river steps from which, until 1867, prisoners sentenced to transportation embarked on their journey to Australia.”
Novelist Henry James called Millbank “a worse act of violence than any it was erected to punish”.

Above: Henry James (1843 – 1916)
The phrase “down under” is said to be derived from a nearby tunnel through which the convicts were walked in chains down to the river.
A section of the tunnel survives in the cellars of the nearby Morpeth Arms, a pub built to seve the prison warden and said to be haunted by the ghost of a former inmate.

Depending on their crime, prisoners could be given the choice of receiving a five-to-ten-year jail sentence instead of exile.
Among the many to be sent to Australia – and perhaps the unluckiest of them all – was Isaac Solomon, a convicted pickpocket and the inspiration for the character Fagin in Charles Dickens´ Oliver Twist.

Above: Isaac “Ikey” Solomon (1727 – 1850)
In 1827 Solomon managed to escape while being taken to Newgate Prison.
He fled England to New York, but then travelled on to Tasmania when he discovered his wife had been transported there for crimes of her own.
Upon arrival in Tasmania, Solomon was rearrested, shipped home to London, retried, reconvicted and sentenced to exiled imprisonment for 14 years….back to Tasmania.
We made our weaving way to Pimlico Tube Station, a unique station in that it doesn´t have an interchange with another Underground or National Rail Line.
We rode the rails until Waterloo, the last station to provide steam-powered services and the busiest railway station in London / the 91st busiest in the world / the busiest transport hub in Europe.
I had once taken the Eurostar from Waterloo Station to Paris as one of the 81,891,738 travellers during the 13 years (1994 – 2007) Eurostar operated from here, before it began service from St. Pancras.
The clock at Waterloo has been cited as one of the most romantic spots for a couple to meet, and has appeared in TV (Only Fools and Horses) and in the film Man Up.

Waterloo Station has appeared in literature (Three Men in a Boat, The Wrong Box, The War of the Worlds), films (Terminus, Rush Hour, Sliding Doors), theatre (The Railway Children), music (the Kinks song “Waterloo Sunset”) and paintings.
Our destination – typical of travelling with a doctor – a hospital, St. Thomas Hospital, noteworthy for a male serial killer and a lady humanitarian.

Dr. Thomas Neill Cream, also known as the Lambeth Poisoner, was a Scottish Canadian serial killer who claimed victims from the United States, England, Canada and Scotland.
Above: Dr. Thomas Neill Cream (1850 – 1892)
Born in Glasgow, Cream was raised outside Quebec City.
He attended Montreal´s McGill University and then did his post-graduate training at St. Thomas.
In 1878 Cream obtained qualifications in Edinburgh.
He then returned to Canada to practice in London, Ontario.
In August 1879, Kate Gardener, a woman with whom he was having an affair, was found dead in an alleyway behind Cream´s office, pregnant and poisoned.
Cream claimed that she had been made pregnant by a prominent local businessman, but after being accused of both murder and blackmail, Cream fled to the United States.
Cream established a medical practice not far from the red light district of Chicago, offering illegal abortions to prostitutes.
In December 1880 another patient died after treatment by Cream, followed by another in April 1881.
On 14 July 1881, Danial Stott died of poisoning, after Cream supplied him a remedy for epilepsy.
Cream was arrested, along with Stott´s wife.
Cream was sentenced to life imprisonment in Joliet prison.
Cream was released in 1891, after Governor Joseph Fifer commuted his sentence.
Using money inherited from his father, Cream sailed for England.
He returned to London and took lodgings at 103 Lambeth Palace Road.
At that time, Lambeth was ridden with poverty, petty crime and prostitution.
On 13 October 1891, Nellie Donworth, a 19-year-old prostitute accepted a drink from Cream.
She died three days later.
On 20 October, Cream met 27-year-old prostitute Matilda Clover.
She died the next morning.
On 2 April 1892, after a vacation in Canada, Cream was back in London where he attempted to poison Louise Harvey.

Above: Louise Harvey
On 11 April, Cream met two prostitutes, Alice Marsh, 21, and Emma Shrivell. 18, and talked his way into their flat.
Cream put styrchine in their bottles of Guinness.

Both women died in agony.
On 3 June 1892, Cream was arrested and was later sentenced to death.
On 15 November, Cream was hanged on the gallows at Newgate Prison and his body buried in an unmarked grave within the prison walls.

Cream´s name does not appear in later McGill graduate directories.
No mention of those who mourned Cream´s victims is made either.
Ladies of the night lost in the shadows of Lambeth lamplight, fallen and forgotten.
Another medical professional is equally remembered at a site as inconspicuous as a prison burial ground: a parking lot.
On the south side of Westminster Bridge, a series of red brick Victorian blocks and modern white additions make up St. Thomas´s Hospital, founded in the 12th century.
At the Hospital´s northeastern corner, off Lambeth Palace Road, is a car park.
A hospital car park isn´t the most obvious location for a museum, but that where one finds the homage to Florence Nightingale, the genteel rebel who invented the nursing profession.

Born on 12 May 1820 at the Villa Colombaia, three decades before Cream, Florence Nightingale was named after the city of her birth, Florence, Italy.

Above: Florence Nightingale (1820 – 1910)
“There is nothing like the tyranny of a good English family.”
Florence was born into a rich, well-connected family though quite liberal in their attitudes.
Their circle of friends and acquaintances included the author Elizabeth Gaskell, the scientist Charles Darwin and the reform politician the Earl of Shaftesbury.
(For the story of the Earl of Shaftesbury, please see Canada Slim and the Outcast of this blog.)
Her maternal grandfather William Smith campaigned to abolish slavery and Florence´s father William Nightingale educated both her and her sister Frances Parthenope (after her birthplace of Parthenope, Naples) in French, Latin, German, mathematics, philosophy and science, then considered strictly male pursuits,
The Nightingales loved to travel – her parents´ honeymoon lasted so long that they produced two daughters before they returned home.
Growing up Florence visited many European cities.
She travelled to France, Switzerland, Germany and Italy.
She enjoyed visiting museums, dancing at balls, and going to concerts, confessing at one point that she was “music mad”.
In 1838, her father took the family on a tour of Europe where they were introduced to the English-born Parisian heiress Mary Clarke, with whom Florence bonded.

Above: Mary Clarke (1793 – 1883)
Clarke was a stimulating hostess who did not care for her appearance, and while her ideas did not always agree with those of her guests, “she was incapable of boring anyone”.
Clarke´s behaviour was said to be exasperating and eccentric and she had no respect for upper class British women, whom she regarded generally as inconsequential.
She said that if given the choice between being a woman or a galley slave, she would choose the galleys.
Clarke generally rejected female company and spent her time with male intellectuals.
However Clarke made an exception in the case of Florence.
They were to remain close friends for 40 years despite their 27-year age difference.
Clarke demonstrated that women could be equals to men, an idea that Florence did not obtain from her mother Fanny Smith.
Florence underwent the first of several experiences that she believed were calls from God in February 1837 while at her family home of Embley Park, prompting a strong desire to devote her life to the service of others.

Above: Embley Park
Devout and scholarly, Florence was not expected to do anything much apart from marry and procreate.
As a young woman, Florence was attractive, slender and graceful.
She had rich brown hair, a delicate complexion and a prominent, almost Roman, nose.

She was slim until middle age and tall for a Victorian woman, about 5´8″ or 172 cm in height.
While her demeanour was often severe, she was very charming and possessed a radiant smile.
Florence received several marriage proposals.
She was certainly not supposed to work, but Florence´s ambition was to become a nurse.
Her parents were aghast.
In the Victorian Age, nurses were known for being devious, dishonest and drunken.
Hospitals were filthy, dangerous places exclusively for the poor.
The rich were treated in the privacy of their own homes.
In her youth Florence was respectful of her family´s opposition to her working as a nurse, but nonetheless she announced her decision to enter the field in 1844.
Despite the intense anger and distress of her mother and sister, Florence rebelled against the expected role for a woman of her status to become a wife and mother.
“I craved for something worth doing instead of frittering time away on useless trifles.”
Florence came closest to accepting the marriage proposal of politician and poet Richard Monckton Milnes, but after a nine-year courtship she rejected him in 1849, convinced that marriage would interfere with her ability to follow her calling to nursing.

Above: Richard Monckton Milnes (1809 – 1885)
Whether Milnes´ devotion to the writing of Marquis de Sade and his extensive collection of erotica had something to do with Florence´s decision remains unstated.
She knew that marriage would mean swapping one cage for another and felt that God meant her to remain single.
“Marriage had never tempted me.
I hated the idea of being tied forever to a life of Society, and such a marriage could I have.”
In the essay Cassandra, Florence wrote about the limited choices facing women like her and raged against the way women were unable to put their energy and intelligence to better use.
Florence´s parents allowed her to visit Rome in 1847 with family friends, Charles and Selina Bracebridge, hopefully to take her mind off nursing.
In Rome, Florence met the young politician, former Secretary of War, Sidney Herbert on his honeymoon with his wife Elizabeth.

Above: Sidney Herbert (1810 – 1861)
Together Florence and Elizabeth visited convents and hospitals run by Catholic nuns.
Sidney and Florence became lifelong close friends and the Herberts would later be insturmental in facilitating Florence´s future nursing work.
Florence continued her travels with the Bracebridges as far as Greece and Egypt.
Her writings on Egypt in particular are testimony to her learning, literaray skill and philosophy of life.
Sailing up the Nile as far as Abu Simbel in January 1850, Florence wrote of the temples there:

Above: The temples of Abu Simbel: the Great Temple of Ramses II (left), the Temple of Nefertari (right)
“Sublime in the highest style of intellectual beauty, intellect without effort, without suffering …. not a feature is correct – but the whole effect is more expressive of spiritual grandeur than anything I could have imagined.
It makes the impression upon one that thousands of voices do, uniting in one unanimous simultaneous feeling of enthusiasm or emotion, which is said to overcome the strongest man.”
At Thebes, Florence wrote of being “called to God”.
A week later near Cairo she wrote in her diary:
“God called me in the morning and asked me would I do good for Him alone without reputation.”
During a visit to the Parthenon in Athens, Florence rescued an owl, which she called Athena.

Above: The Parthenon
Athena always perched on Florence´s shoulder or in her pocket, with a specially designed pouch to to catch her droppings.
Above: Athena (1850 – 1855)
Athena was a demanding creature who had to be bathed with sand daily.
When the badtempered owl died, Florence wrote:
“Poor little beastie, it was odd how much I loved you.”
Her sister Frances wrote a short story, The Life and Death of Athena, ensuring the little owl´s posthumous fame.
Rather than forget nursing as her parents hoped, Florence´s determination grew even stronger.
Later in 1850, Florence visited the Lutheran religious community at Kaiserswerth-am-Rhein, near Dusseldorf, in Germany, where she observed Pastor Theodor Fliedner and the deaconesses working for the poor and the sick in a hospital, orphanage and college.

Above: Kaiserswerth Clinic
She regarded the Kaiserswerth experience as a turning point in her life, where she received months of medical training which would form the basis for her later care.
Florence learned about medicines, how to dress wounds, observed amputations and cared for the sick and dying.
She had never felt happier.
“Now I know what it is to love life.”
On 22 August 1853, Florence took the post of Superintendant at the Institute for the Care of Sick Gentlewomen in Upper Harley Street in London, a position she held until October 1854.
When an epidemic of cholera broke out in London, Florence rushed to nurse victims in the nearby Middlesex Hospital.
Florence read about the disaster facing the British army in the autumn of 1854.
Hundreds of soldiers were sent to fight with the French and the Ottoman Turks against the Tsar´s Russian army in the Crimea were dying of disease.
The Crimean War was the first time the public could read in the newspapers about how the troops were suffering.

Above: Map of the Crimean War (Russian version)
When the news broke of the disaster in the Army, polticians were criticised.
More soldiers were dying from disease, and from cold during the winter, than from enemy action.
“In most cases the flesh and clothes were frozen together.
As for feet, the boots had to be cut off bit by bit, the flesh coming off with them.”
The wounded arrived by the boatloads at the British Army´s base hospitals at Scutari in Constantinople (today´s Istanbul).
Reporting from the front lines in the Crimea, William Howard Russell, Times journalist, blamed disorganization and a lack of supplies.
Fellow Times journalist in Constantinople, Thomas Chenery, reported that the French allowed women to nurse, unlike the British.
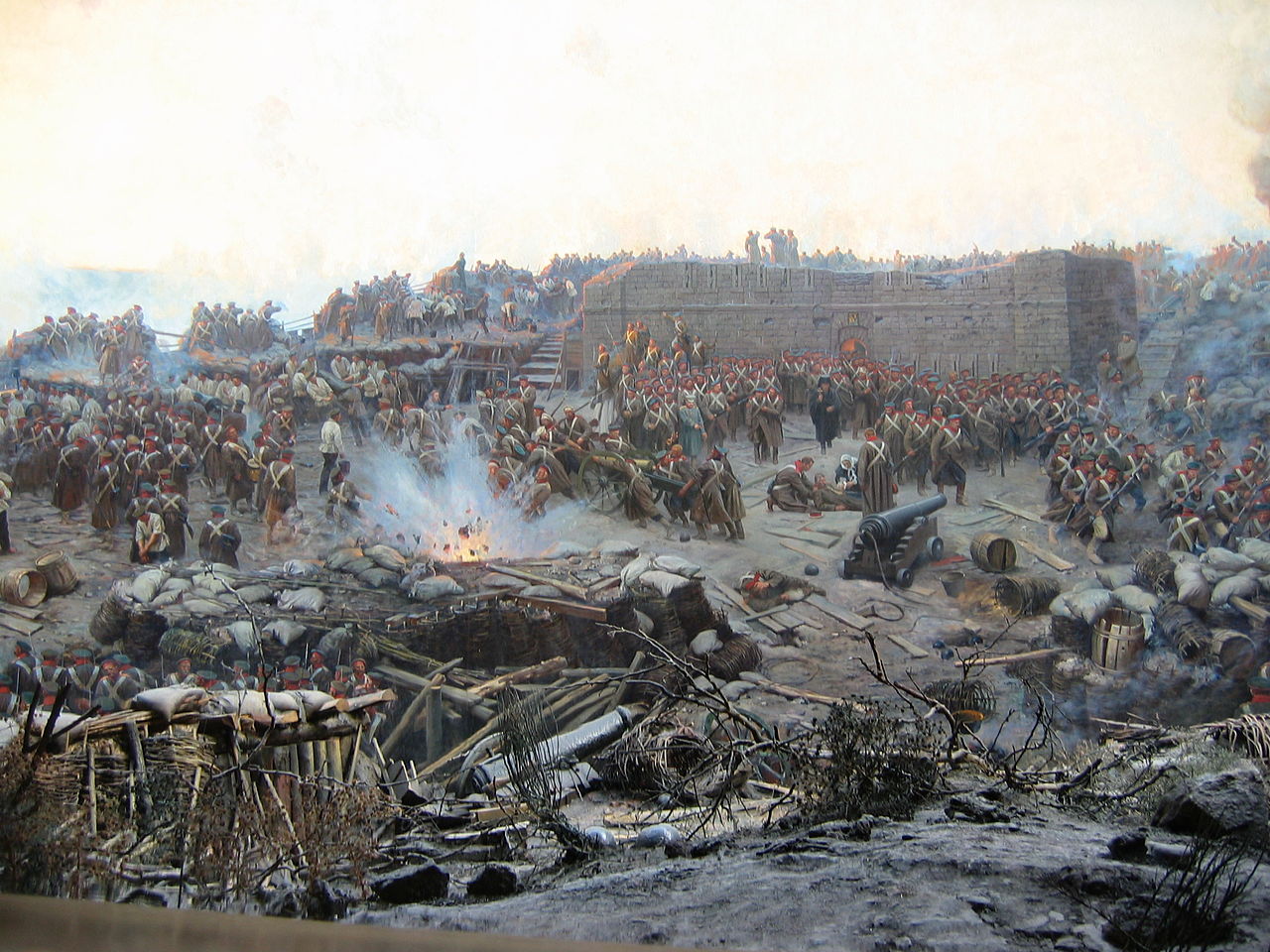
After the initial battles in the Crimea, the conflict centred on the besieged port of Sebastopol, where Russian and Ukranian women nursed heroically.
Above: The Siege of Sebastopol (September 1854 – September 1855), by Franz Roubaud (1902)
Conditions in the vast hospitals were horrific.
“Must men die in agony unheeded?”, demanded the Times.
The scandal provoked a public outcry.
Sidney Herbert, once again Secretary of War, wrote to Florence asking her to lead a group of women nurses – a new and risky idea.
Florence and her team of 38 brave women volunteer nurses that she trained and 15 Catholic nuns set sail for Scutari.
Florence arrived early November 1854 at Selimiye Barracks in Scutari and found that poor care for wounded soldiers was being delivered by overworked medical staff in the face of official indifference.

Medicines were in short supply, hygiene was being neglected and mass infections were common, many of them fatal.
There was no equipment to process food for the patients.
There was a lack of food, a lack of blankets, a lack of beds.
Casualities arrived, after a long journey, dirty and starving.
“It is of appalling horror!
These poor fellows suffer with unshrinking heroism, and die or are cut up without complaint.
We are steeped up to our necks in blood.”
At Scutari the nurses had to contend with rats, lice, cockroaches and an absence of sanitation and had to cope with long hours and hard physical work.
After Florence sent a plea to the Times for a government solution to the poor condition of the facilities, the British Government commissioned engineer Isambard Kingdom Brunel to design a prefabricated hospital that could be built in England and shipped to the Dardanelles.

Above: Isambard Kingdom Brunel (1806 – 1859)
The result was Renkioi Hospital, a civilian facility that had a death rate less than one tenth that of Scutari.
Florence reduced the death rate from 42% to 2% by making improvements in hygiene.
She implemented handwashing and other hygiene practices in the war hospital.
She organized the nurses and soldiers´ wives to clean shirts and sheets and the men to empty the toilets.
She bombarded Herbert with letters asking for supplies and used her own money and funds sent by the public via the Times, to buy scrubbing brushes and buckets, blankets, bedpans and operating tables.
“This morning I foraged in the purveyor´s store – a cruise I make almost daily, as the only way of getting things. I am really cook, housekeeper, scavenger, washerwoman, general dealer and storekeeper.”
Every night she walked miles of hospital corridors where thousands of casualities lay, holding a Turkish lantern (fanoos) on her nightly rounds of the wards.

Florence would always dismiss the idea that she alone improved the Hospital.
It was a team effort.
In Britain, penny papers popularised the image of “the Lady with the Lamp” patrolling the wards.

Her work went beyond nursing care.
Florence treated the soldiers equally, whatever their rank, and also thought of their families´ welfare.
She wrote letters of condolence to relatives, sent money to widows, and answered inquiries about the missing or ill.
When the initial crisis was over, Florence also organized reading rooms.
As an alternative to alcohol, the Inkerman Café was opened, serving non-alcoholic drinks.
She set up a banking system so ordinary soldiers could send their pay home, rather than drink or gamble it away.
Stories of Florence´s devotion to the men flooded home to Britain.
One soldier wrote home of the love and gratitude for Florence felt by “hundreds of great rough soldiers”.
The men worshipped her.
During her first winter at Scutari, 4,077 soldiers died.
Ten times more soldiers died from diseases such as typhoid, typhus, cholera and dysentary than from battle wounds.
Scutari had been built on top of a huge cesspool.
With overcrowding eased, defective sewers flushed out and ventilation improved, death rates were sharply reduced.
Florence still believed that the death rates were due to poor nutrition, lack of supplies, stale air and overworking of the soldiers.
She came to believe that most of the soldiers at the hospital were killed by poor living conditions.
Florence believed that she needed to maintain military style discipline over her nurses.
“If a patient is cold, if a patient is feverish, if a patient is faint, if he is sick after taking food, if he has a bed-sore, it is generally the fault not of the disease but of the nursing.”
She wanted her nurses to be treated with respect by the men and doctors.
This meant no flirting with doctors or soldiers, no disobedience or drunkenness.
The first image showing Florence as “the Lady with the Lamp” appeared in the Illustrated London News early in 1855.
As the war dragged on, Florence´s work made her internationally famous.
“She is a ministering angel without any exaggeration in these hospitals, and as her slender form glides quietly along each corridor, every poor fellow´s face softens with gratitude at the sight of her.
When all the medical officers have retired for the night and silence and darkness have settled down upon those miles of prostrate sick, she may be observed alone, with a little lamp in her hand, making her solitary rounds.”
Florence hated what she called the “buzz fuzz” of celebrity, but she knew how to use public opinion.
Fame gave her power and influence to make changes, but she knew it obscured the achievements of others and the human cost of the war.
Florence´s image appeared as pottery figurines, souvenirs and even on paper bags.
Songs and poems were written about her.
When the US poet Henry Wadsworth Longfellow published “Santa Philomena” in 1857, it fixed Florence´s image forever as the Lady with the Lamp.

Above: Henry Wadsworth Longfellow (1807 – 1882)
“Lo! in that house of misery
A lady with a lamp I see
Pass through the glimmering gloom
And flit from room to room.”
After contracting “Crimean fever” from infected goat´s milk, Florence suffered ill health.
After the Crimean War, Florence returned to Britain in August 1856, travelling under the name “Miss Smith” to avoid publicity.
Thin, exhausted and ill, she felt a sense of failure and grieved over the soldiers who did not return.
“My poor men lying in your Crimean graves, I stand at the altar of murdered men.
Florence devoted the rest of her life to ensure that they did not die in vain.

While Florence shrank from public appearances, she skillfully used her reputation and the authority of her name to convincethose in power of the need for health reform, starting with Queen Victoria, whom she impressed greatly when they met in Balmoral.

Above: Queen Victoria (1819 – 1901)
For the rest of her days she would continue to suffer reoccuring bouts of fever, exhaustion, depression, loss of appetite, insomnia and severe back pain.
Unable to continue nursing, she devoted herself to health reform, founded the first training school for nurses at St. Thomas, campaigned to improve hospital conditions and championed the cause of midwives.
Often irritable, highly critical of herself and others, Florence worked on, writing hundreds of letters, gathering and analysing statistics, commenting on reports, briefing politicians and medical experts.
Prompted by the Indian mutiny of 1857, Florence began a lifelong campaign to improve the health of all Indians, not just British soldiers.
She studied the design of hospitals in Britain and across Europe.
Florence wrote Notes on Nursing to help ordinary women care for their families.
She stressed the importance of cleanliness, warmth, fresh air, light and proper diet.
Florence wrote some 200 books, pamphlets and articles, and over 14,000 letters.
As well as nursing she wrote about religion and philosophy, sanitation and army hygiene, hospitals, statistics and India.
She wrote about her travels and the frustrations of life for educated women.
Florence changed society´s ideas about nursing.
She believed in looking after a person´s mental as well as physical wellbeing.
She stressed the importance of being sensitive to a patient´s needs and their environment to aid recovery.
She helped make nursing a respectable profession for women.
Her work proved an inspiration to many, including the founder of the Red Cross movement, Henri Dunant.

Above: Henri Dunant (1828 – 1910)
Florence championed causes that are as just important today as they were in her day, from hospital hygiene and management, to the nursing of soldiers during war and afterwards, and healthcare for all around the world.
In recognition of her pioneering work in nursing, the Nightingale Pledge is taken by new nurses.

The Florence Nightingale Medal is the highest international distinction a nurse can achieve and the annual International Nurses Day is celebrated around the world on her birthday.
The Florence Nightingale Museum doesn´t just celebrate Florence as a devout woman who single-mindedly revolutionized the healthcare industry but as well it hits the right note by putting the two years she spent tending to the wounded of the Crimean War in the context of a lifetime of tireless social campaigning, and also mentions others involved in that same health care crisis.
Dimly lit and curiously curated with circular display cases covered in fake grass or wrapped in bandages, this small museum is packed with fascinating exhibits, from Florence´s hand-written ledgers and primitive medical instruments to pamplets with titles like How People May Live and Not Die in India.
The Museum and the neighbourhood of Lambeth are worth exploring, especially in a world too full of Dr. Creams and too few Florence Nightingales.
Perhaps if our politicians visited more museums like the Red Cross Museum in Geneva or the Florence Nightingale Museum there might less incentive to cause war ourselves or to ignore wars far removed from us, such as Yemen – “a pointless conflict (that) has caused the world´s worst humanitarian crisis”.
Perhaps if we followed role models such as Florence we might one day truly find peace on Earth and good will towards man.
Sources: Wikipedia / The Rough Guide to London / Rachel Howard and Bill Nash, Secret London: An Unusual Guide / Simon Leyland, A Curious Guide to London / Florence Nightingale Museum / http://www.florence-nightingale.co.uk









