Landschlacht, Switzerland, Tuesday 10 December 2019
There are things in Switzerland (and in our existence) that we simply take for granted:
And the thing about Swiss stereotypes is that some of them are true.
Diplomatic?
Yes.
Efficient?
Absolutely.
Boring?
Only at first glance.
Despite being one of the most visited countries in Europe, Switzerland remains one of the least understood.
It is more than simply the well-ordered land of cheese, chocolate, banks and watches.
It is more than a warm summer mountain holiday upon a cobalt blue lake, more than skiing down the slopes of some vertiginous Alp, more than postcard pristine beauty.
It is easy for the tourist to remain blissfully unaware of Swiss community spirit, that it speaks four official languages, that it possesses stark regional differences from canton to canton, that it has exubrant carnivals, culinary traditions and sophisticated urban centres.

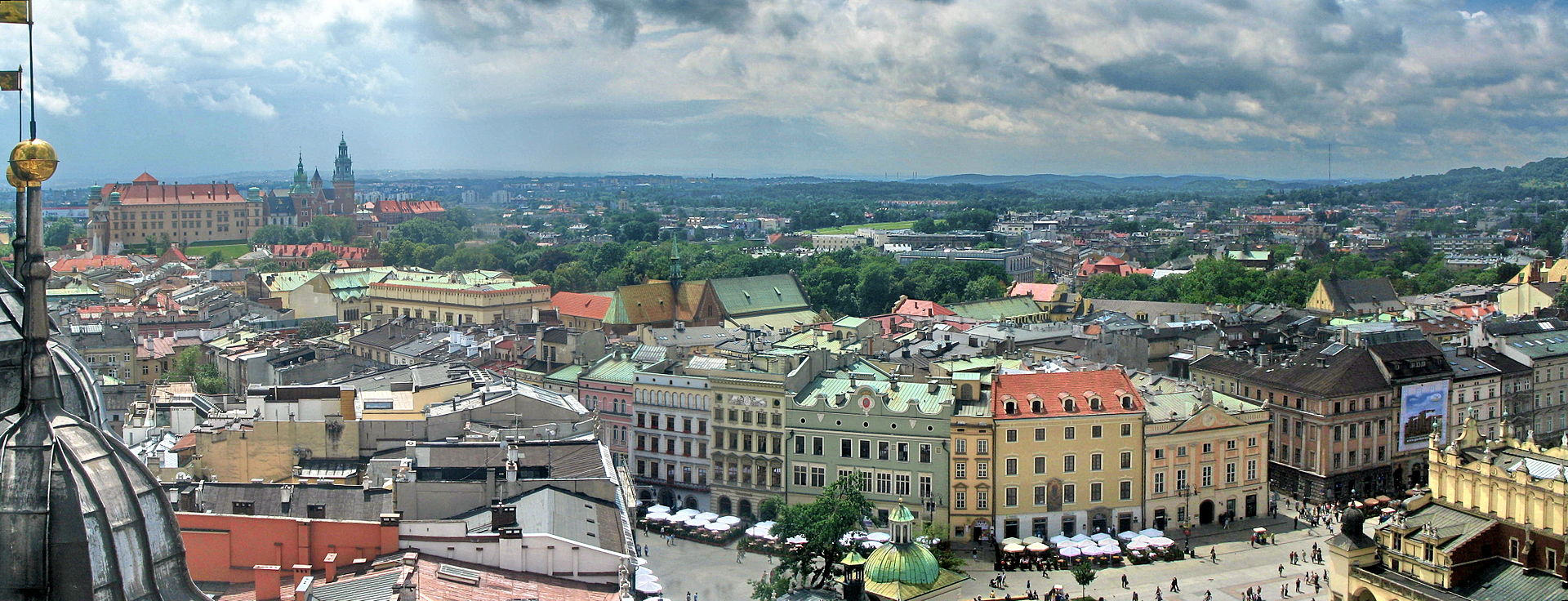
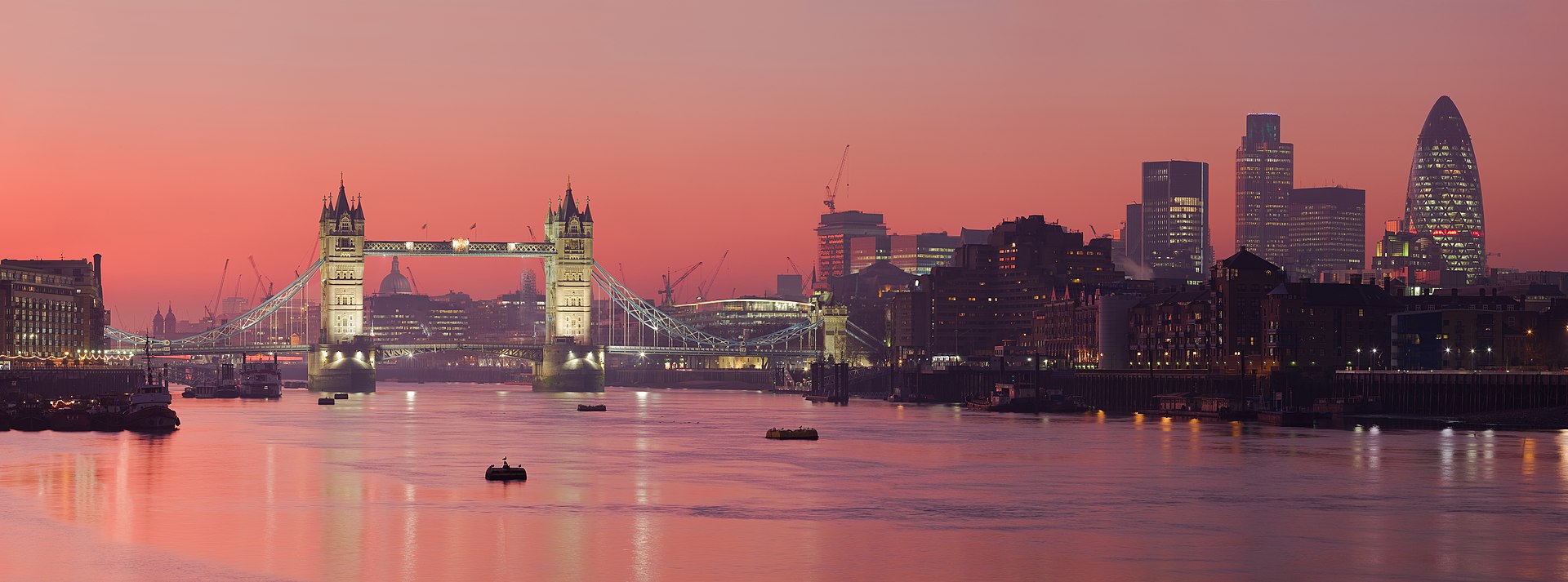
With its beautiful lakeside setting, Geneva (Genève) is a cosmopolitan city whose modest size belies its wealth and importance on the world stage.
French-speaking and Calvinistic it is a dynamic centre of business with an outward-looking character tempered by a certain reserve.
Geneva’s major sights are split by the Rhône River that flows into Lake Geneva (Lac Léman) and through the city’s several distinct neighbourhoods.
On the south bank (rive gauche), mainstream shopping districts Rive and Eaux-Vives climb from the water’s edge to Plainpalais and Vieille Ville, while the north bank (rive droite) holds grungy bars and hot clubbing Pâquis, the train station area and some world organizations.

A little over 1 km north of the train station is the international area, home to dozens of international organizations that are based in Geneva – everything from the World Council of Churches to Eurovision.
Trains and buses roll up to the Place des Nations.
Gates on the Place des Nations open to the Palais des Nations, now occupied by UNOG, the United Nations Office at Geneva, the European headquarters of the United Nations, accessible only to visitors who sign up for a tour.
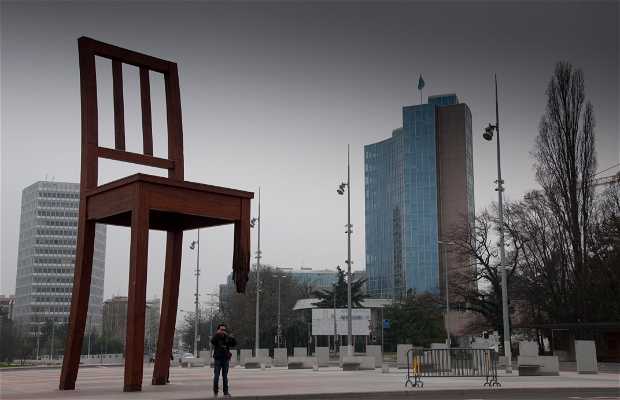
The huge monolith just off the square to the west, that looks like a bent playing card on its edge, is WIPO (the World Intellectual Property Organization), the highrise to the south is ITU (the International Telecommunications Union), just to the east is UNHCR (the United Nations High Commission for Refugees), and so on, and so on, and so on, an infinite combination of letters of the alphabet in an infinite variety of abbreviations and acronyms.
The giant Broken Chair which looms over the square was installed in 1997 for the international conference in Ottawa (Canada’s capital) banning the use of land mines, a graphic symbol of the victims of such weapons.
Geneva is also the birthplace of the International Red Cross / Crescent / Crystal Movement.
And it was the latter, along with the International Museum of the Reformation, that compelled me to visit Geneva.
(For details about the Musée Internationale de la Réforme, please see Canada Slim and the Third Man in my other blog, The Chronicles of Canada Slim.)
Genevè, Suisse, mardi le 23 janvier 2018
Housed within the HQ of the International Committee of the Red Cross (ICRC), the Musée International de la Croix-Rouge et du Croissant Rouge chronicles the history of modern conflict and the role the Red Cross has played in providing aid to combatants and civilians caught up in war and natural disasters.
Enter through a trench in the hillside opposite the public entrance of UNOG and emerge into an enclosed glass courtyard beside a group of bound and blindfolded stone figures.
The stone gathering represents the continual worldwide violation of human rights.
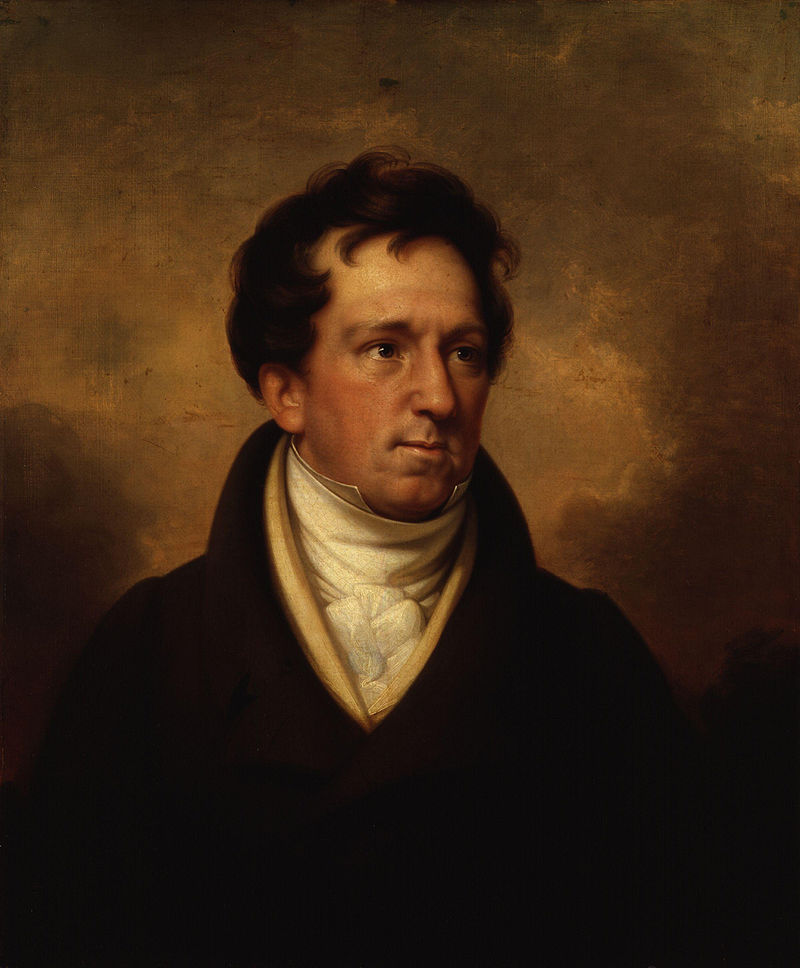
Inside, above the ticket desk, is a quotation in French from Dostoevsky:
“Everyone is responsible to everyone else for everything.”
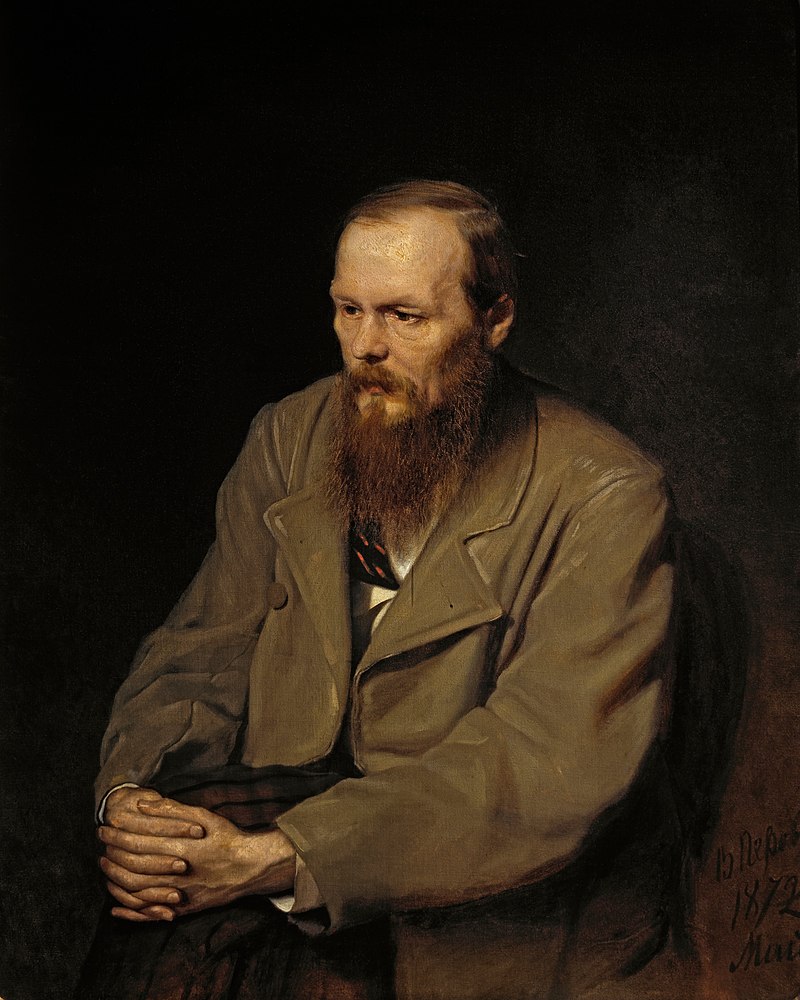

Above: Fyodor Dostoevsky (1821 – 1881)
A free audioguide takes you through the Museum.
Twenty-five years ago, Laurent Marti, a former ICRC delegate, had the idea of creating the International Red Cross and Red Crescent Museum.
Above: Laurent Marti
Marti won the wives of US President Ronald Reagan and Soviet Premier Gorbachev over to his cause in a bid to obtain the support of their respective countries, together with that of local and international societies and personages and of various multinational companies representing a full range of human activities.
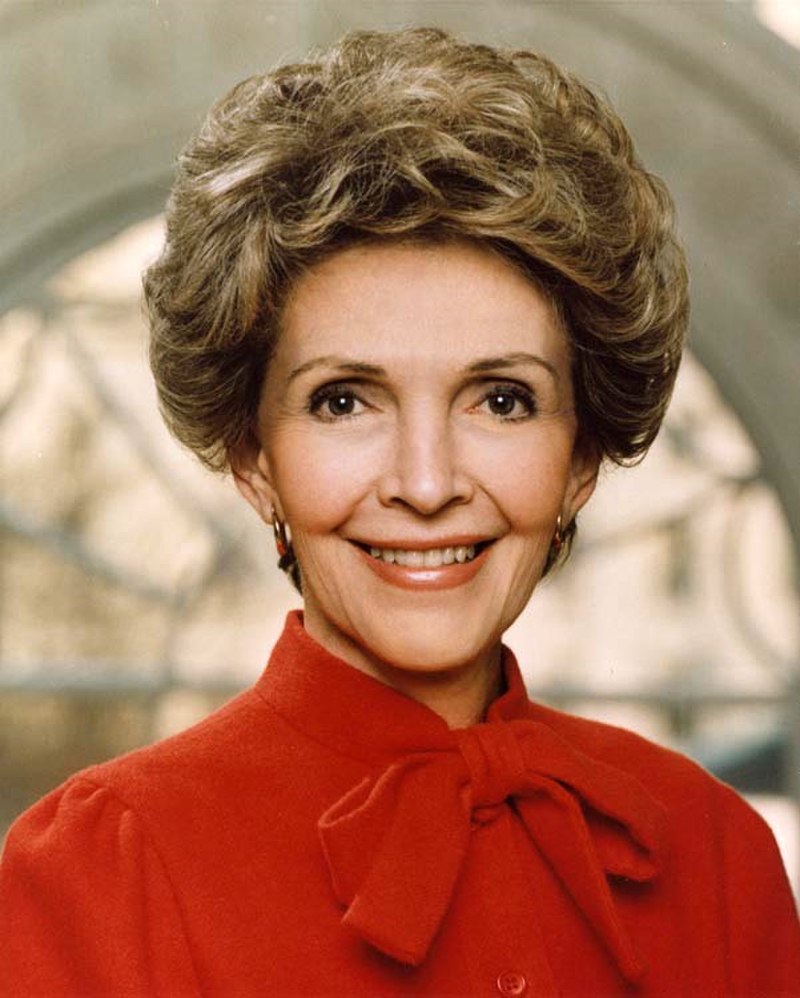

Above: Nancy Reagan (née Davis) (1921 – 2016)

Above: Raisa Gorbacheva (née Titarenko) (1932 – 1999)
The goal of the Museum is to emanate a very powerful atmosphere where no one leaves without having been shaken and deeply moved by what they had seen.
Suffering, death, wounds and mutiliations can be followed by a time of healing, restoration, reunification and an opportunity to be happy again, a right that seemed to have been withdrawn.
Of course, the scars remain deep within the human soul, but the hope of restoration and of a return to normalcy is the message of the Museum.
The International Red Cross and Red Crescent Movement is dedicated to preventing and alleviating human suffering in warfare and in emergencies, such as earthquakes, epidemics and floods.
The Movement is composed of the International Committee of the Red Cross (ICRC), the International Federation of Red Cross and Red Crescent Societies, and the 188 individual national societies.
Each has its own legal identity and role, but they are all united by seven fundamental principles:
- humanity
- impartiality
- neutrality
- independence
- voluntary service
- unity
- universality
The interactive chronology covers one and a half centuries of history, starting with the creation of the Red Cross.
For each year, the events listed include:
- armed conflicts which caused the death of more than 10,000 people and/or affected more than one million people
- epidemics and disasters that caused the deaths of more than 1,000 people and/or affected more than one million people
- significant events in the history of the Movement
- cultural and scientific milestones

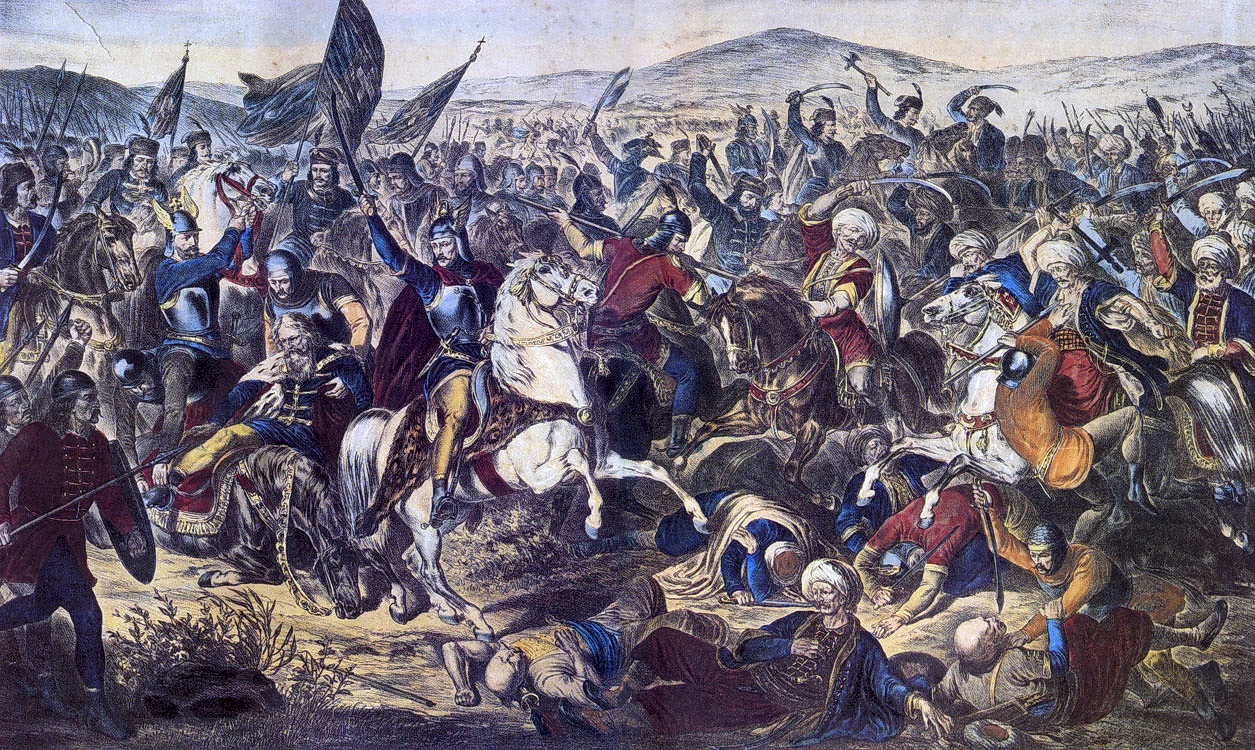
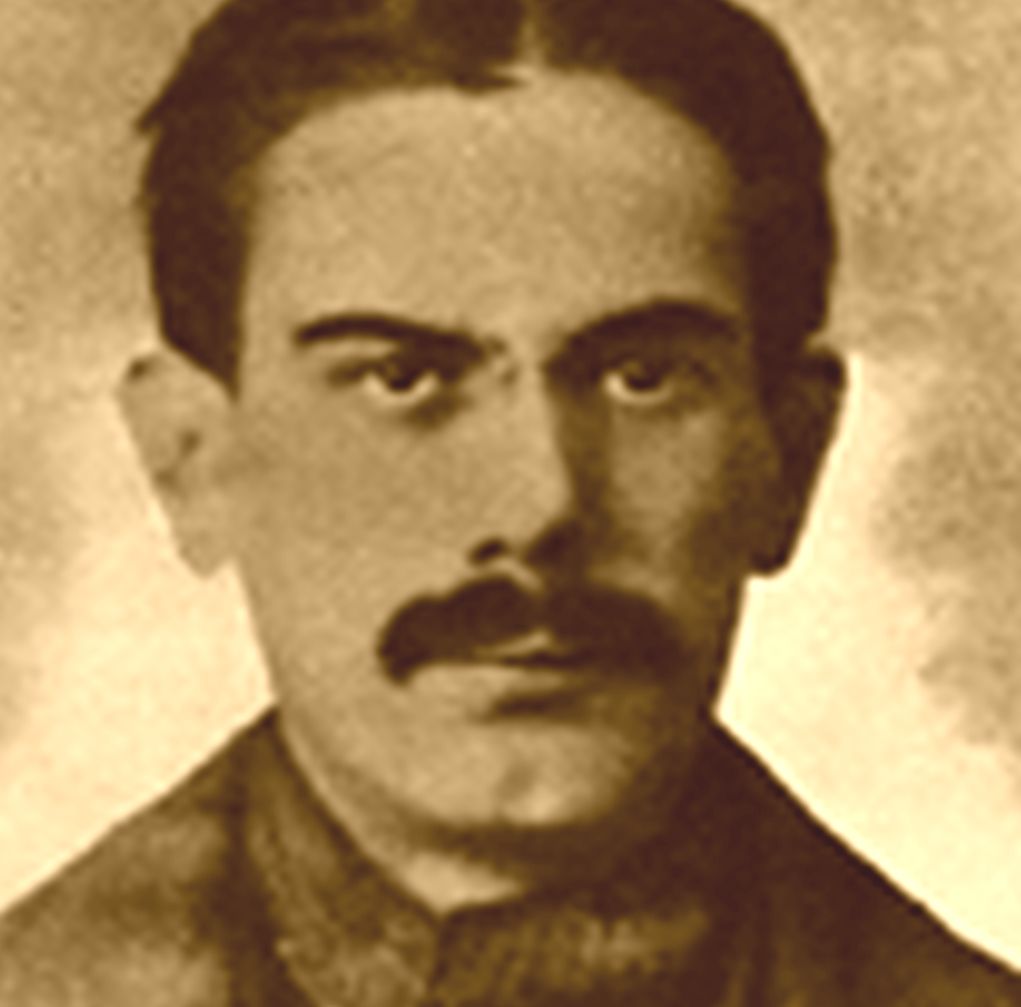
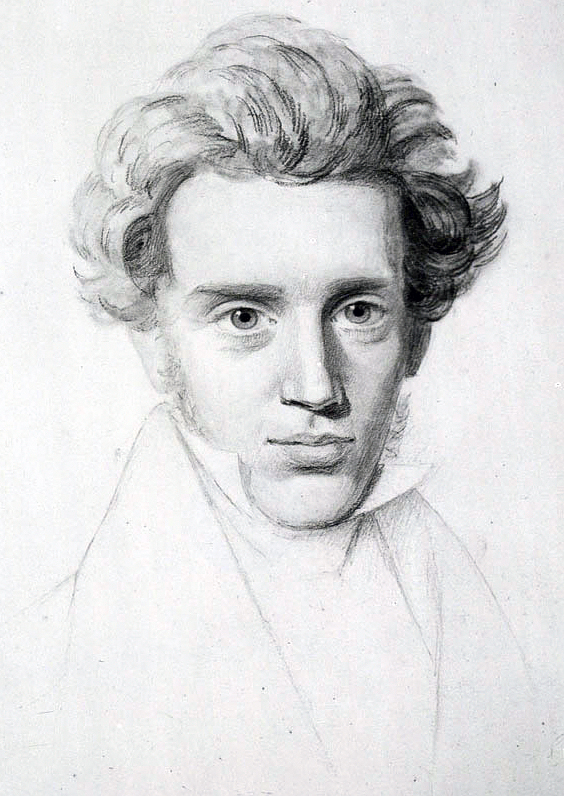
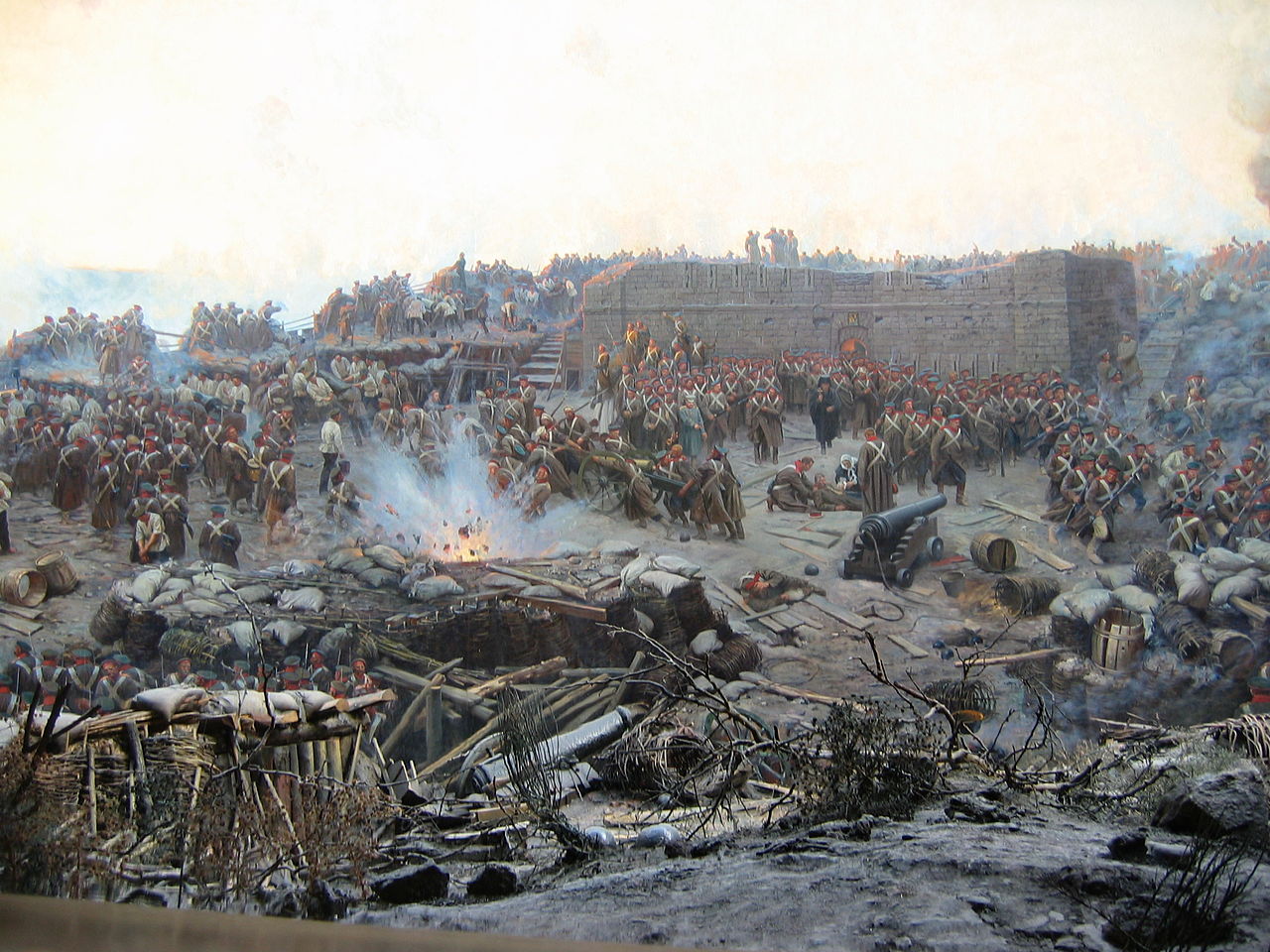
In 1859 Henri Dunant was travelling on business through northern Italy.

Above: Henri Dunant (1828 – 1910)
He found himself close to the Solferino battlefield just after the fighting.
The battle of Solferino was a key episode in the Italian Wars.

With the support of France under Napoleon III, Victor Emmanuel II of Savoy, King of Piedmont, endeavoured to unite the different Italian states.
In spring 1859 the Piedmont forces clashed with the Austrian Empire, which had control over Lombardy and Venetia.
On 24 June 1859, the Franco-Piedmontese troops defeated the Austrians at Solferino, in a battle that left more than 40,000 dead and wounded.
Overwhelmed by the sight of thousands of wounded soldiers left without medical care, Dunant organized basic relief with the assistance of the local people.

“On that memorable 24th of June 1859, more than 300,000 men stood facing each other.
The fighting continued for more than 15 hours.
No quarter is given.
It is a sheer butchery, a struggle between savage beasts.
The poor wounded men that were picked up all day long were ghastly pale and exhausted.
Some, who had been the most badly hurt, had a stupified look.
How many brave soldiers, undettered by their first wounds, kept pressing on until a fresh shot brought them to earth.
Men of all nations lay side by side on the flagstone floors of the churches of Castiglione.
The shortage of assistants, orderlies and helpers was cruelly felt.
I sought to organize as best I could relief.
The women of Castiglione, seeing that I made no distinction between nationalities, followed my example.
“Siamo tutti fratelli” (we are all brothers), they repeated feelingly.

Above: Ossuary of Solferino
But why have I told of all these scenes of pain and distress?
Is it not a matter of urgency to press forward to prevent or at least alleviate the horrors of war?
Would it not be possible, in time of peace and quiet, to form relief societies given to the wounded in wartime?
Societies of this kind, once formed and their permanent existence assured, would be always organized and ready for the possibility of war.
Would it not be desirable to formulate some international principle, sanctioned by a Convention inviolate in character, which, once agreed upon and ratified, might constitute the basis for societies for the relief of the wounded?”

Above: Ossuary of Solferino
Back home in Geneva, Dunant wrote A Memory of Solferino.
The book was published in 1862 and was an immediate success.

In it, Dunant made two proposals:
- the formation of relief societies which would care for wounded soldiers
- the establishment of an international convention to guarantee their safety
Those ideas led, the following year, to the foundation of the Red Cross, and ten months later to the first Geneva Convention.

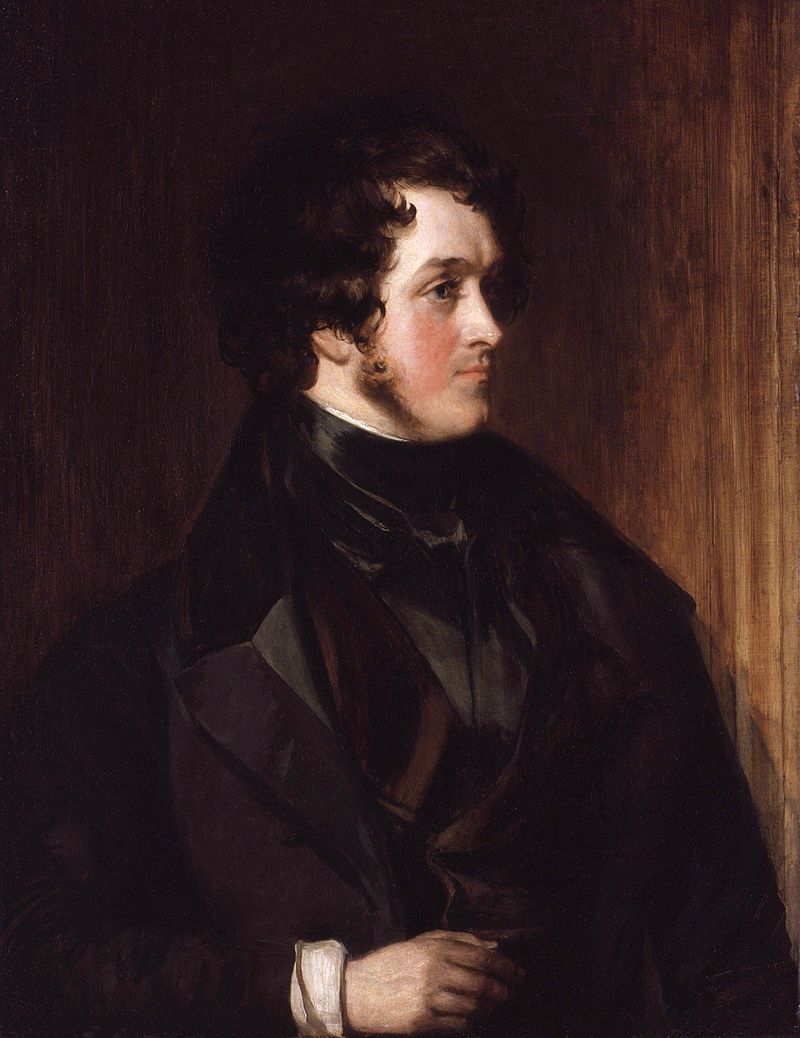
In 1863, in response to Dunant’s appeal, Gustave Moynier persuaded the Geneva Public Welfare Society to consider the possibility of training groups of volunteer nurses to provide relief for the wounded.
A committee was set up, the International Committee for Relief to the Wounded, the future ICRC, was born.
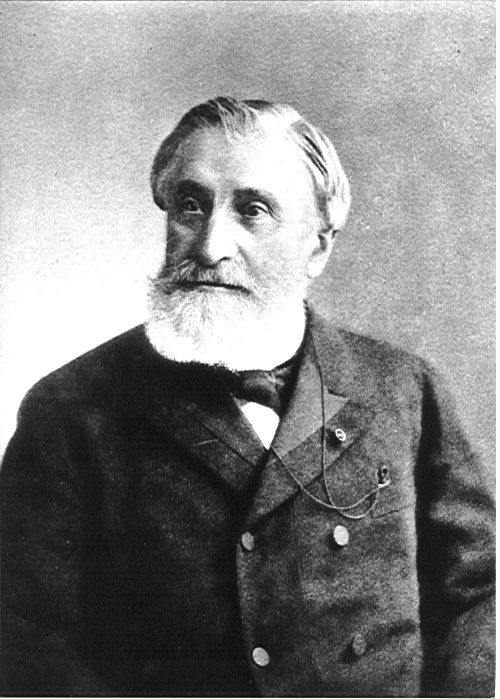

Above: Gustave Moynier (1826 – 1910)
The need to defend human dignity has been a constant concern throughout history.
From the Code of Hammurabi (1750 BC) to the Universal Declaration of Human Rights (1948), texts from all periods and cultures exist to testify to that.
Those texts were frequently written in response to incidents in which human dignity was shown no consideration – slavery, chemical weapons, civilian bombing, concentration camps, atomic bombing, sexual violence, landmines, child soldiers, prisoners with no legal status.
Throughout time mankind has determined:
- that the strong should not suppress the weak (Code of Hammurabi – Mwaopotamia 1750 BC)

Above: Stele of the Code of Hammurabi
- that peace is possible between warring nations (Treaty of Kadesh, the oldest peace treaty known to man and the first written international treaty – Egypt 1279 BC)

Above: Treaty of Kadesh
- that we should be free to practice our own religions (Cyrus Cylinder – Persia 539 BC)
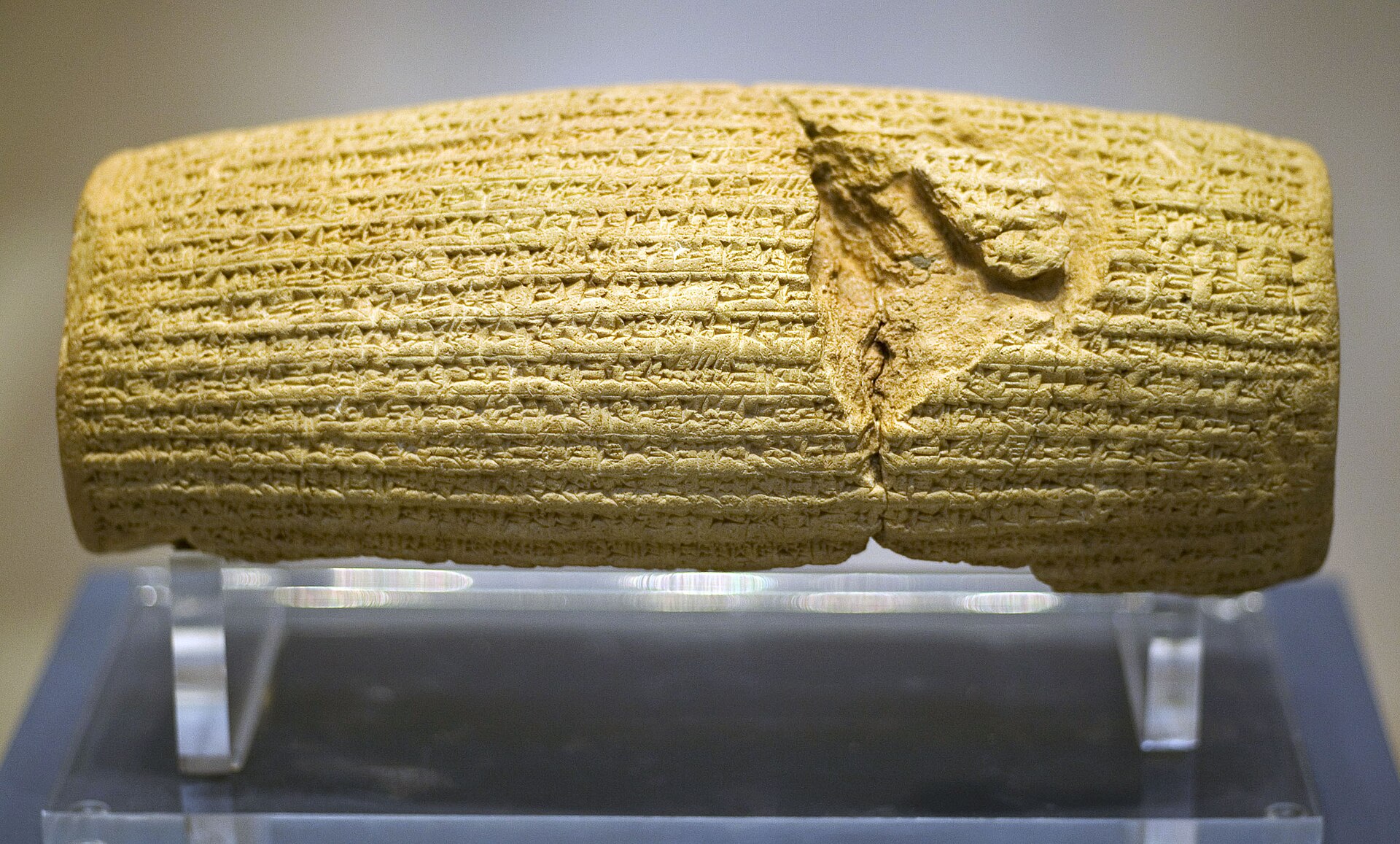

Above: Cyrus Cylinder
- that we should not do unto others what we don’t wish done to ourselves (The Analects of Confucius – China 480 BC)
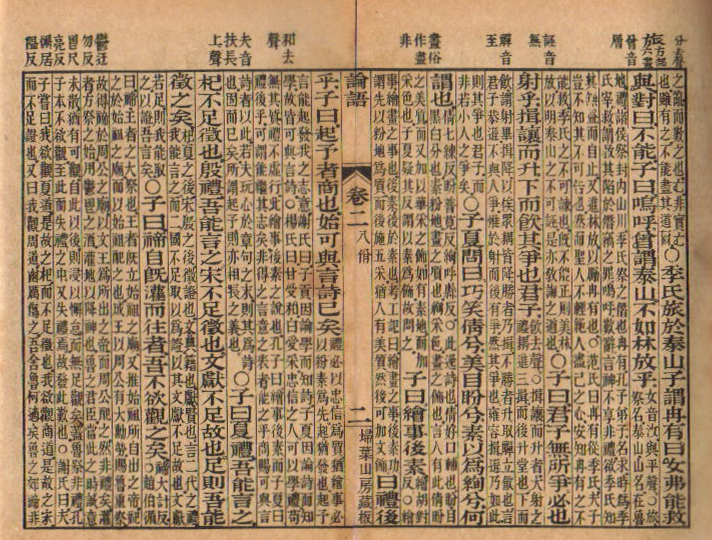
Above: The Analects
- that we should live lives of non-violence with respect towards all (The Edicts of Ashoka – India 260 BC)

Above: The Edicts of Ashoka
- that power should not be used arbitrarily nor imprisonment without just cause (The Magna Carta – England 1215)

Above: Magna Carta
- that all persons are free and that no one is a slave to another (The Manden Charter – Mali 1222)
Above: The Manden Charter
- that women and children and the insane have dignity and rights that must be respected (The Viqayet – Muslim Spain 1280)
- that mankind has natural and inalienable rights (freedom, equality, justice, community) (Declaration of the Rights of Man and of the Citizen – France 1789)

- that the wounded need to be treated regardless of nationality, that all human beings are free and equal in dignity and in rights (Universal Declaration of Human Rights – United Nations 1948)

The original title of the initial Geneva Convention was the Convention for the Amelioration of the Condition of the Wounded in Armies in the Field.
It had only ten articles and one sole objective:
To limit the suffering caused by war.
Article 7 provided for the creation of the protective emblem of the red cross.
This document laid the foundations of international humanitarian law, marks the start of the humanitarian adventure.
By 2013, 194 nations are party to the Geneva Conventions of 12 August 1949.
(See http://www.icrc.org for the complete list.)

The Museum explains how the Geneva Conventions developed from one man’s battlefield encounter.
After Dunant’s publication of A Memory of Solferino in November 1862, Gustave Moynier (1826 – 1910), chairman of the Geneva Public Welfare Society, in response to Dunant’s appeal, persuaded Society members the following February to consider the possibility of training groups of volunteer nurses to provide relief for the war wounded.
An ad hoc committee was set up – the International Committee for Relief to the Wounded.
The future ICRC was born.

Above: ICRC Headquarters, Geneva
“Ambulances and military hospitals shall be recognized as neutral and as such protected and respected by the belligerants as long as they accommodate wounded and sick.” (Article 1)
“Inhabitants of the country who bring help to the wounded shall be respected and shall remain free.” (Article 5)
“Wounded or sick combatants, to whatever nation they may belong, shall be collected and cared for.” (Article 6)
“A distinctive and uniform flag shall be adopted for hospitals, ambulances and evacuation parties.” (Article 7)
A red cross on a white background was adopted in 1863, followed by a red crescent, a red lion and red sun (1929) and a red crystal (2005).




To protect the victims of conflict, the ICRC has at its disposal several instruments defined by international humanitarian law.
“At all times, parties to the conflict shall, without delay, take all possible measures to search for and collect the wounded and sick.”
“The civilian population as such, as well as individual civilians, shall not be the object of attack.”
“The parties to the conflict shall endeavour to conclude local agreements for the passage of medical personnel and medical equipment.”
“Civilian hospitals may in no circumstances be the object of attack.”
“It is prohibited to commit any acts of hostility directed against historic monuments, works of art or places of worship.”
“Works or installations containing dangerous forces, namely dams, dykes and nuclear stations shall not be made the object of attack.”
“It is prohibited to attack, destroy, remove or render useless objects indispensible to the survival of the civilian population.”

Above: The Red Cross in action, 1864
The Second World War (1939 – 1945) involved 61 countries in war and caused the death of around 60 million people, more than half of whom were civilians.
In 1945 more than 20 million people had been displaced.
In 1995 the ICRC publicly described its attitude to the Second World War Holocaust as a “moral failure“.
Above: Images of World War II (1939 – 1945)
The persecution of the Jews by the Nazis began shortly after Hitler came to power in 1933 and subsequently continued to intensify, culminating in systematic extermination from 1942 onwards.

Above: Auschwitz, Poland, May 1944
At the time, the ICRC had no legal instrument to protect civilians.
The 1929 Convention relative to the Treatment of Prisoners of War applied only to members of the armed forces.
The organization thus considered itself powerless in the face of the anti-Semitic fury of the Nazi dictatorship.

Thus in October 1942 the Committee refused, in particular, to launch a public appeal on behalf of civilians affected by the conflict.
Although the International Red Cross endeavoured to provide aid for Jewish civilians, it erred on the side of caution.

Above: Jewish women, occupied Paris, June 1942
It was not until the spring of 1944 that a change of strategy took shape.
As Germany’s war efforts collapsed, ICRC delegates belatedly managed to enter some concentration camps, becoming voluntary hostages in order to prevent the further massacre or forced evacution of the prisoners.

Above: Auschwitz, May 1944
The harsh lesson of the Second World War had been learned.
In 1949 the Fourth Geneva Convention was adopted:
It provides protection for civilians during armed conflict.
It was complemented in 1977 by additional protocols which reinforce the protection given to victims of armed conflicts, international or domestic.
In particular, the additional protocols established the distinction between civilians and combatants.
In an armed conflict, the ICRC’s mandate is to ensure respect for the Geneva Conventions.
When the ICRC observes serious violations of the Conventions, it points them out to the countries concerned in confidential reports.
However, on occasion, that information has been published in the press:
- Le Monde during the Algerian War

Above: Images of the Algerian War (1954 – 1962)
- The Wall Street Journal about Abu Ghraib Prison

Above: Lynndie England with “Gus“, Abu Ghraib Prison, Iraq
- The New York Review of Books / Wikileaks about Guantanamo Prison

Above: Guantanamo “Gitmo” Prison, Cuba
Such leaks put the ICRC in a difficult position as discretion is a necessary part of its work and its discussions with the authorities.
Its confidentialiy policy actually facilitates access to detainees, wounded people and groups of civilians.
When humanitarian diplomacy fails, the ICRC then resorts to a more open form of communication.
It then issues press releases publicly condemning serious violations of the Conventions.
In the 1980s the United Nations Security Council set up ad hoc tribunals to judge the crimes committed in former Yugoslavia and in Rwanda.
In 1998 the International Criminal Court (ICC) was established.
It was a permanent institution with the power to open investigations, to prosecute and to try people accused of committing war crimes, genocide or crimes against humanity.
The ICC began its work in 2005 by opening three investigations into crimes:
- in the Democratic Republic of the Congo
- in Uganda
- in the Sudan
The existence of a permanent international court gives the world the means of determining facts and of punishing those responsible for the crimes.
It gives victims an opportunity to have their voice heard.

Above: Logo of the International Criminal Court
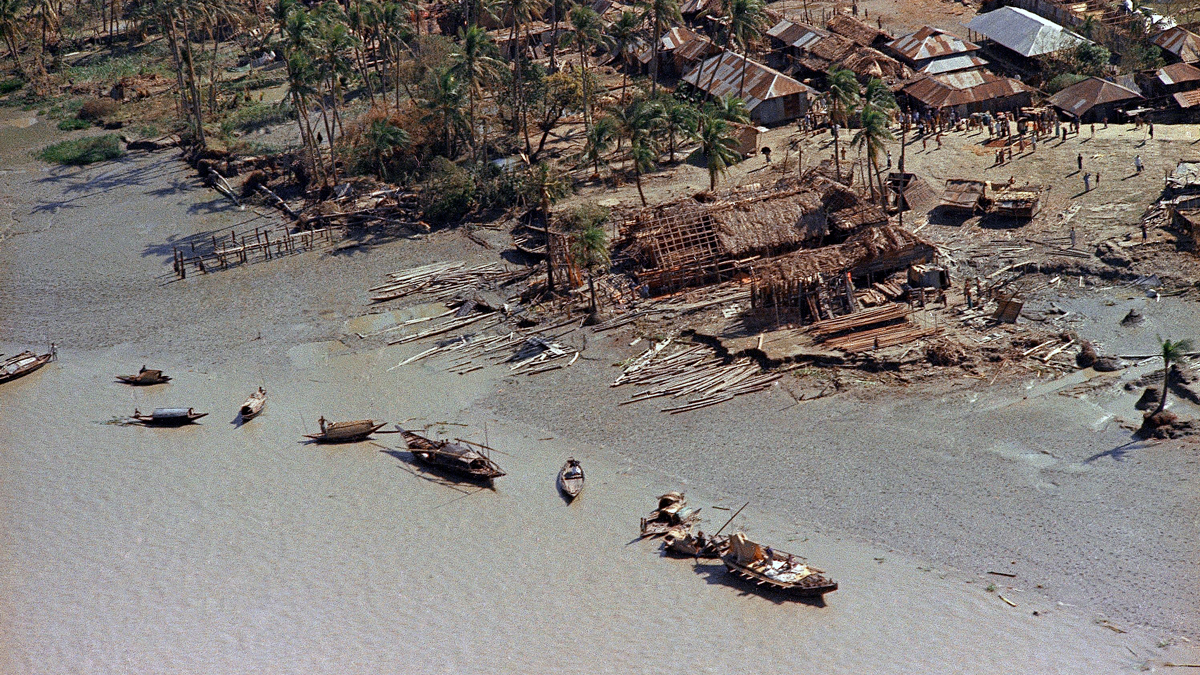
Poverty, migration, urban violence….
All of them are present-day threats to human dignity.
All over the world, large sections of the population are living in extremely precarious hygenic conditions.
Economic changes are forcing more and more people to emigrate.
Those migrants, who frequently have no identity documents, are exploited and ostracized.
In some megacities, whole districts are at the mercy of armed groups which terrorize the inhabitants.
Each of those situations presents a challenge to which a response must be found.

Above: Syrian refugees, Ramtha, Jordan, August 2013
Since the First World War, the ICRC has had the right to visit prisoners of war and civilian detainees during an international armed conflict.
In other situations, the right to meet prisoners must be negotiated with the authorities.
Visiting prisons, talking to the detainees and making lists of their names are ways of preventing disappearances and ill treatment.
After each prison visit, ICRC delegates write a report.
They must have access to all places of detention and be allowed to repeat their visits as often as necessary.
The visits always follow the same procedure.
Following a meeting with those in charge of the prison, the delegates inspect the premises: cells, dormitories, toilets, the exercise yard, the kitchen and any workshops.
They draw up a list of prisoners and interview them in private without witnesses.
At the end of the visit, the delegates inform those in charge of the prison of their observations.
They then prepare a confidential report for the authorities.
The visitor sees many photographs of prison visits, including those to a German POW camp in Morocco, to French POWs in a German Stalag, political detainees in Chile, detainees in Djibouti….
But it is items from these visits given by prisoners to the ICRC delegates that tell far more emotional stories.
Some examples:
- a model village showing ICRC activities in Rwanda
- a doll figure of a female delegate made in an Argentinian prison
- a pearl snake made by Ottoman prisoners
- a necklace with a Red Cross pendant made by a lady prisoner in Lebanon
- a ciborium (a container for Catholic mass hosts – symbols of the body of Christ) made of bread by Polish prisoners of conscience
- a bar of soap carved into the shape of a detainee in a cell made by a Burmese artist imprisoned for suspected ties to the opposition party
An installation in the Museum that followed seemed somewhat incongruous….
Therein the visitor can change and produce large flows of different colours by touching a wall.
The idea is that the larger the number of visitors, the richer the flow of colours, so as to provide an interactive experience that appeals to people’s senses, emotions and feelings, thus all visitors become part of a colourful celebration of human dignity.
Honestly….
This felt more like a gimmick to capture children’s hyperactive attention than an exhibit that strengthens human unity, designed more to entertain than educate.
Human beings are social beings who are defined by their links with others.
When those links are broken, we lose part of our identity and our bearings.
Of the many activities the ICRC performs, the giving and receiving of news and finding one’s loved ones again are understood to be elements of stability that are critical during crisis situations.
This Museum has, like the Reformation Museum in this city, as other museums in other cities and countries I have visited, its own Chamber of Witnesses – video testimonials whose lifelike likenesses are meant to invoke within the voyeur a sense of how we are not unlike those speaking with us electronically.
We see Toshihiko Suzuki, a dentist and specialist in craniofacial anatomy, tell us how he identified victims of the 2011 tsunami.
We learn of the experience of Sami El Haj, an Al Jazeera journalist held in Guantanamo from 2002 to 2008.
We consider the life of Liliose Iraguha, a survivor of the Rwandan genocide.
We marvel at the resilience of human beings by listening to Boris Cyrulnik, a French neuropsychiatrist and ethologist.
During a conflict or a natural disaster, many people are cut off from their families – by capitivity, separation or disappearance.
Tracing one’s loved ones and passing on one’s news become basic needs.
Originally intended for victims of war, the ICRC tracing services subsequently expanded to include persecuted civilians.
More recently, tracing activities have been extended to families who have become separated as a result of natural disasters or migration.
The International Prisoners of War Agency (1914 – 1923) was established by the ICRC, shortly after the start of the First World War – which involved 44 states and their colonies and caused the death of more than 8 million people, 20 million wounded and in the immediate post-war period of epidemics, famine and destitution another 30 million deaths.
Organised in national sections, its archives contain six million index cards that document what happened to two million people: prisoners of war, civilian internees and missing civilians from occupied areas.
The cards contain information about individual detainees. when they were taken captive, where they were held and, if relevant, when they died.
People who were without news of a loved one could present a request to the Agency, which would then send them what information it had.
Today the Agency’s documents are still used to reply to requests from families as well as to enquiries from historians.
And, as far as I could tell, the Agency is now in the Museum.
It contains:
- 5,119 boxes with 6 million index cards
- 2,413 files containing information provided by the belligerents
- 600,000 pages filling 20 linear metres of general files
This location is fitting for it was in the Rath Museum in Geneva where the Agency once was.
In all, more than 3,000 volunteers, most of them women, worked there during the conflict.
During the War, the Agency dispatched 20 million messages between detainees and their families and forwarded nearly 2 million individual parcels as well as several tonnes of collective relief.
The Agency’s role was also to obtain the repatriation of prisoners who had been taken captive in breach of the Geneva Conventions: doctors, nurses, stretcher bearers and military chaplains.
It helped to ensure that the wounded were returned home or interned in neutral countries.
The pacifist writer Romain Rolland was one of the Agency’s first volunteers:
“Its peaceful work, its impartial knowledge of the actual facts in the belligerent countries, contribute to modify the hatred which wild stories have exasperated and to reveal what remains of humanity in the most envenomed enemy.”

Above: Romain Rolland (1866 – 1944)
It was not until the end of the Second World War that Europe realized the extent of the tragedy affecting civilians.
The International Tracing Service (ITS) was then established.
The ITS has files on more than 17 million people: civilians persecuted by the Nazis, displaced persons, children under the age of 18 who had become separated from their families, forced labourers and people held in concentration camps or labour camps.
The ITS was set up in Bad Arolsen, Germany, and has helped millions of people to trace their loved ones.

Above: International Tracing Services, Bad Arolsen, Germany
Nowadays, the need to trace missing people also extends to the victims of natural disasters and to migrants, using not only index cards, but photo tracing (used to find nearly 20,000 children missing during the 1994 genocide in Rwanda), distributions of name lists (for example, the Angola Gazette – a list of people who went missing during the Angolan Civil War from 1975 to 2002) and the Internet (for example, http://www.familylinks.icrc.org).
Despite all tracing efforts, sometimes missing people do not get found, do not go home.
In that case, receiving confirmation of death puts an end to uncertainty and enables families to begin the process of mourning and to start to rebuild their lives.
The erection of memorials is one way of honouring the dead and of giving them a place of dignity in the collective memory.
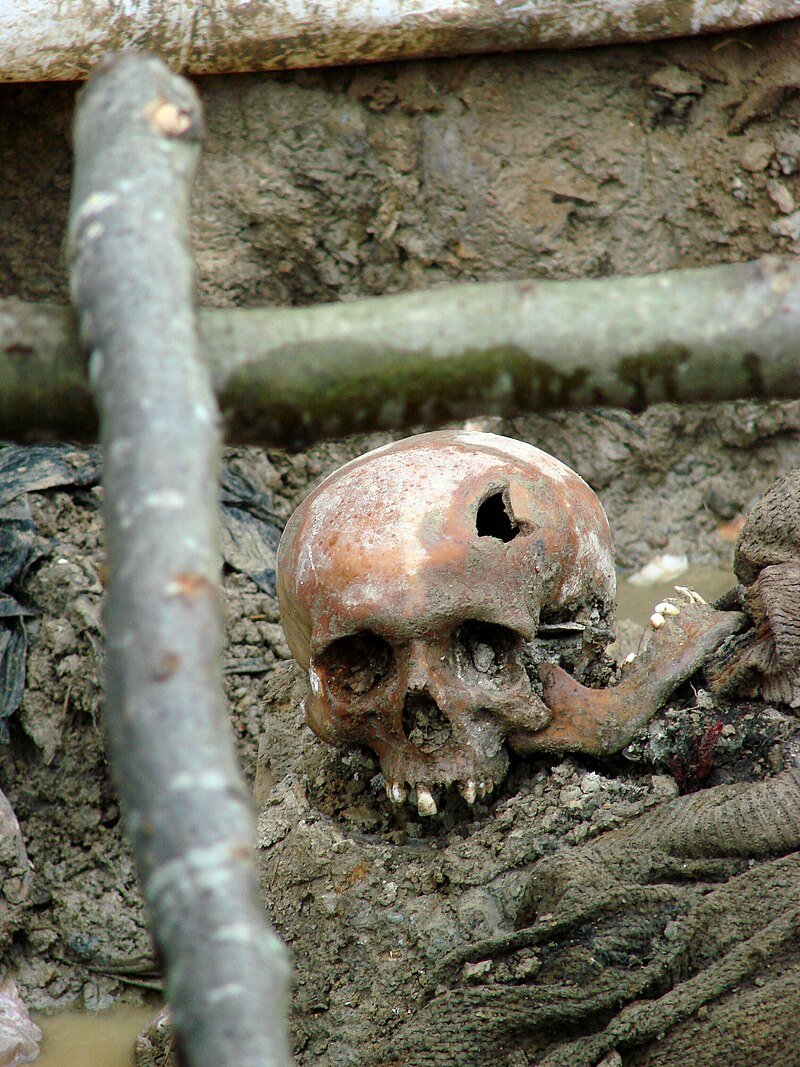

For example, in 1995 the city of Srebrenica was attacked by forces under the command of General Radko Mladic.

Mladic had the women and children of this refuge of hounded Muslim civilians separated from the men and forced to leave Srebrenica.
The men were hunted down and killed.
More than 8,000 people went missing.
By 2010 only 4,500 victims had been identified and buried.

When faced with a collective tragedy and without a dead body, families are completely at a loss.
A memorial is sometimes their only means of paying tribute to the dead, of giving them a place in the collective consciousness and of recalling the events that led to those disappearances.
Examples include victims from:
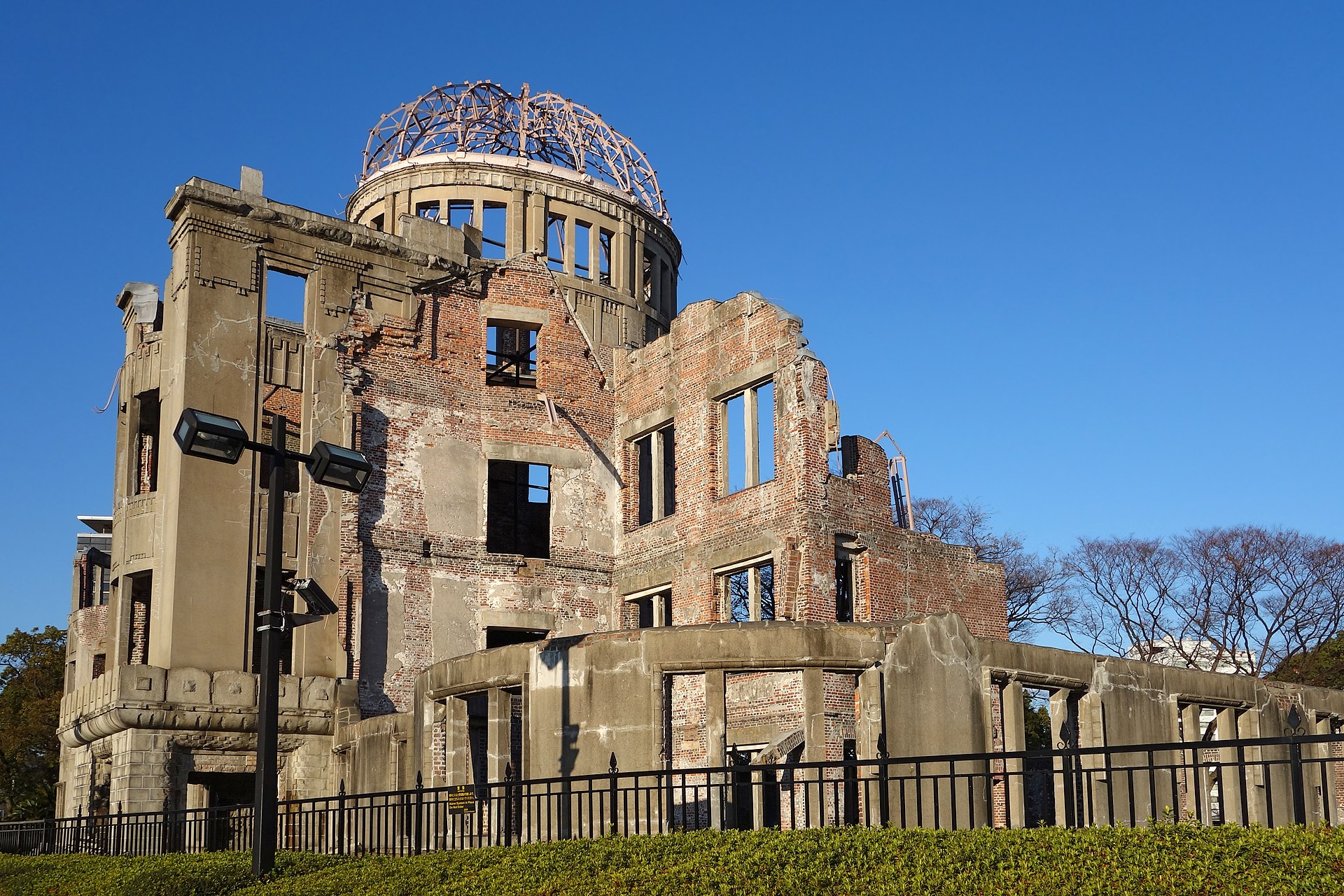
- the 1945 atomic bombing of Hiroshima
Above: Hiroshima Peace Memorial (Genbuko Dome)
- the deportation of Jews from France

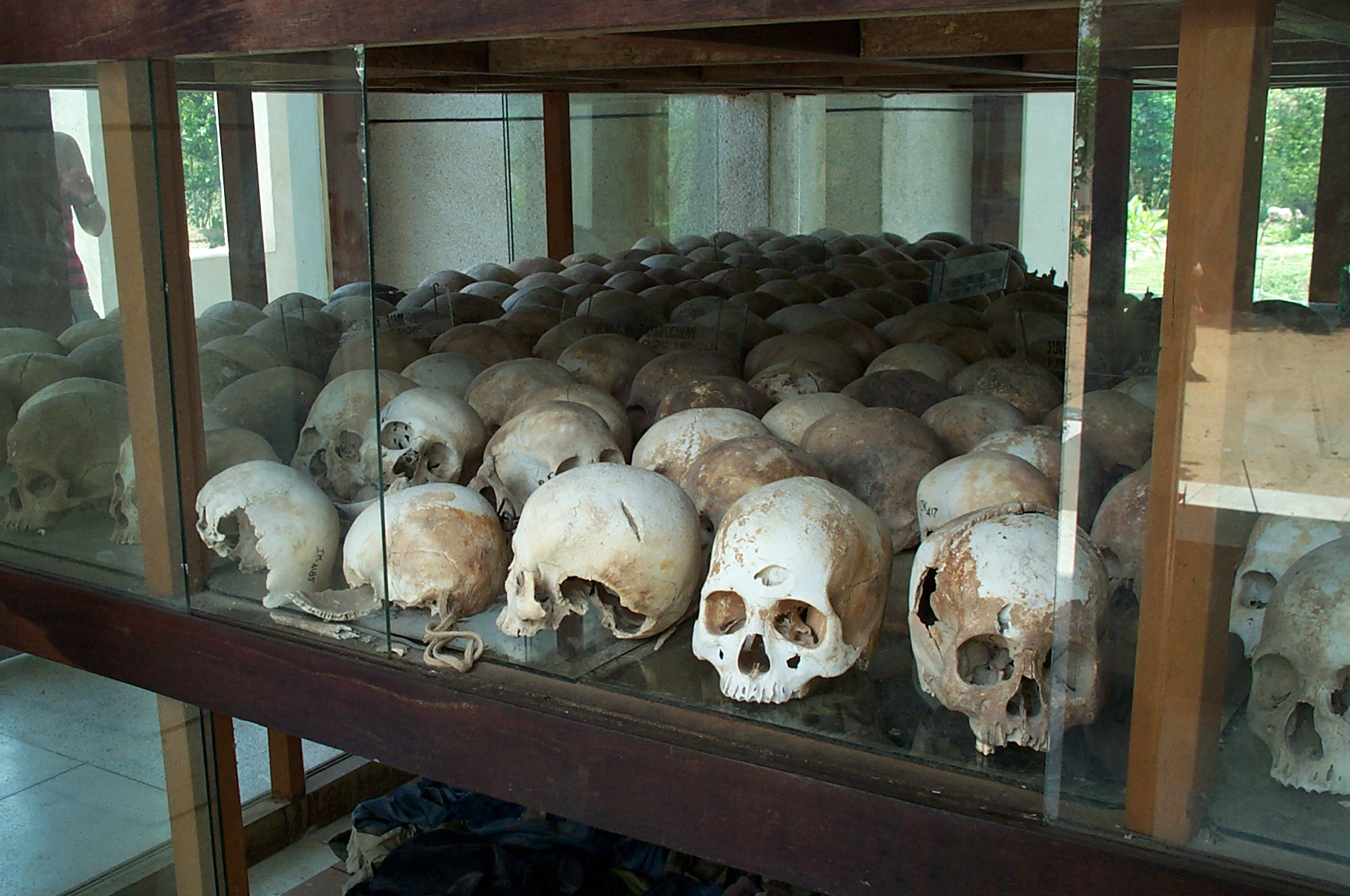
- the Khmer Rouge regime in Cambodia

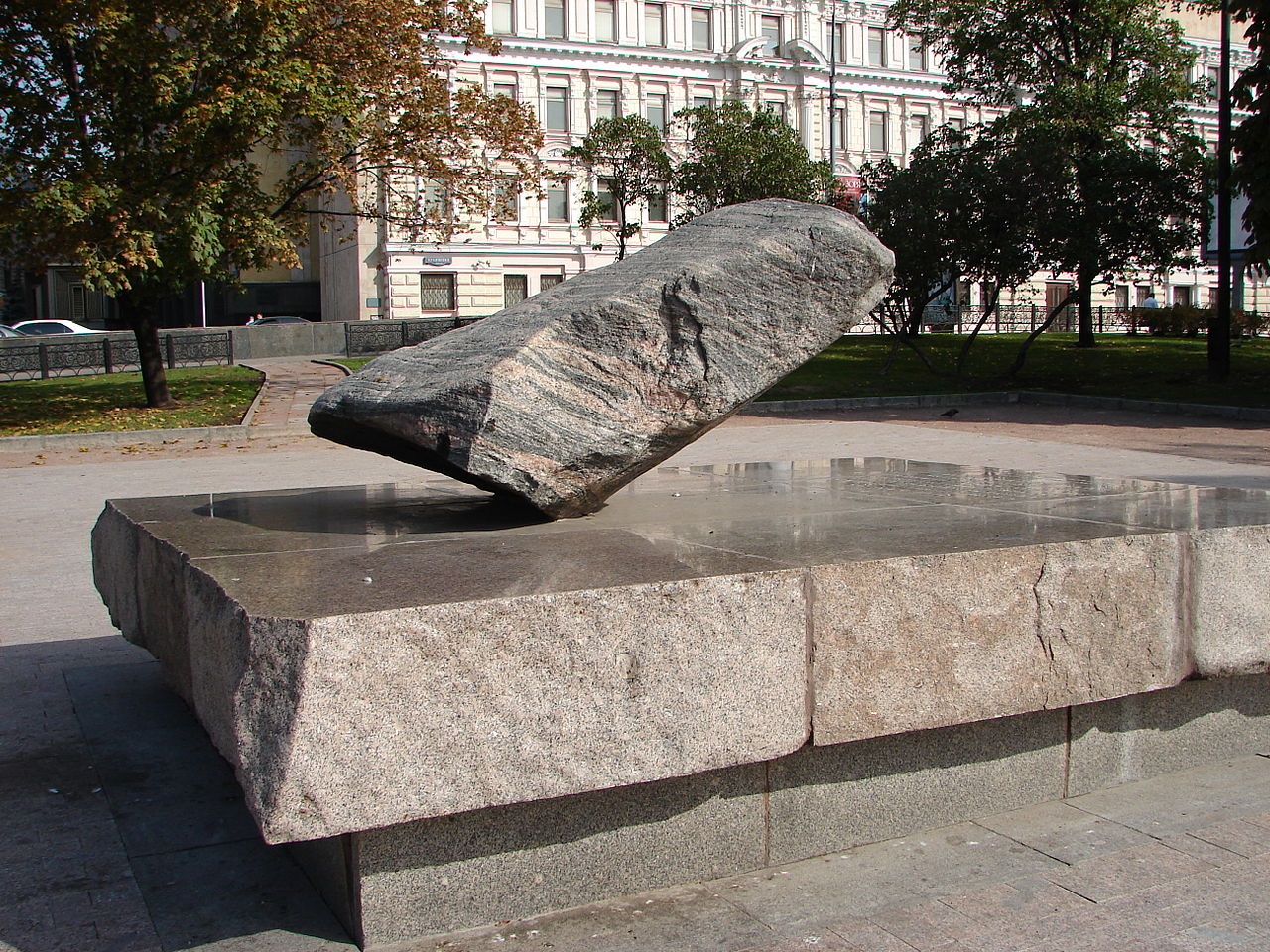
- the Soviet gulags

- the nuclear disaster in Chernobyl, Ukraine
- the civil war in Peru
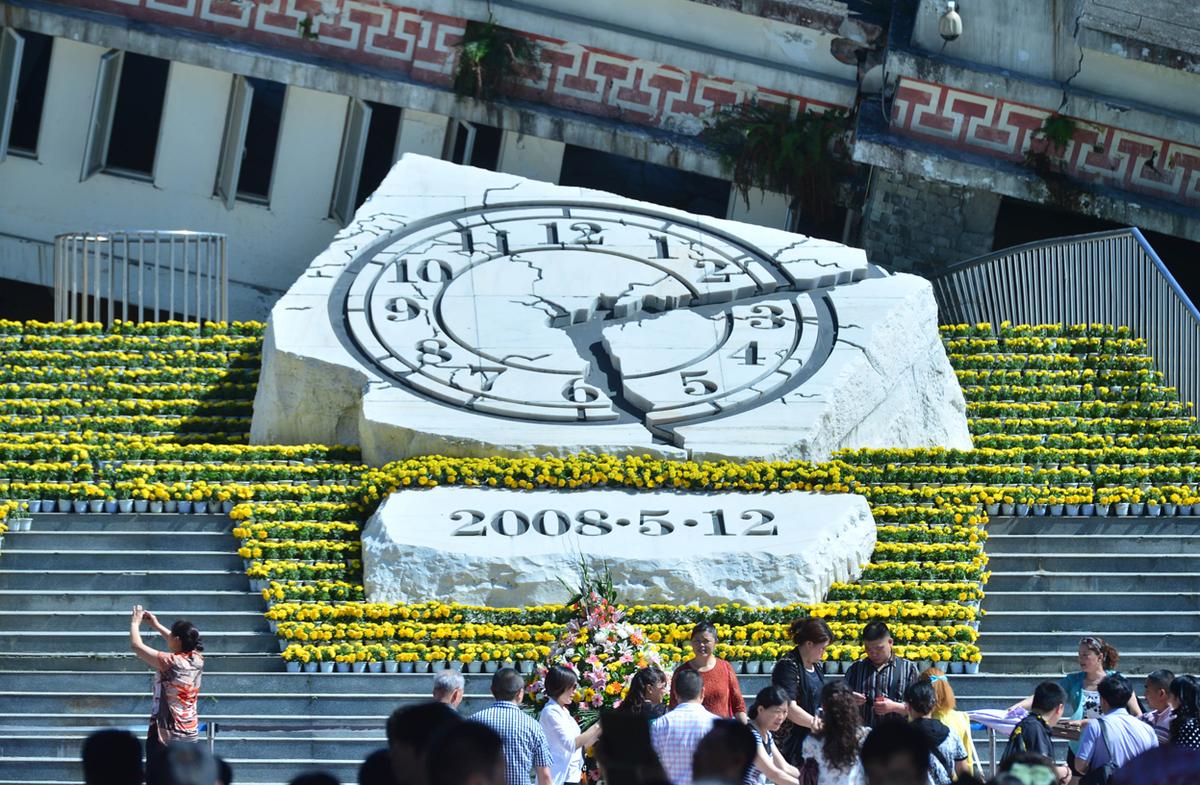
- the earthquake in Sichuan, China
- the 9/11 attack in New York City

Communication is often disrupted during a conflict or a natural disaster.
In circumstances like that, receiving news from one’s family is a source of joy and relief.
There are different ways of sending news:
- Red Cross messages (in use for more than a century)
- Radio messages
- Videoconferencing
- Satellite telephones
A Red Cross message is a short personal missive that was first used in the Franco-Prussian War (1870 – 1871).
It is still in use today.
Each year, thousands of messages are distributed in more than 65 countries with the help of the ICRC.
To make sure that they reach the addressees, messengers sometimes travel long distances to extremely remote areas.
The messages themselves are generally very simple.
The main thing is to enable people to pass brief news on to their loved ones – their state of health, their place of shelter or detention.
For example, the Museum shows messages:
- sent by a French POW to his godmother in Switzerland
- exchanged by a French POW in Morocco and Algeria and his family in France
- written by aircraft passengers taken hostage in Jordan in 1970
- illustrated by children during the Yugoslav conflict in 1994
- by a Sudanese detainee in Guantanamo
- from a Greek child refugee following the Cyprus conflict of 1974
- from a mother to her son in Liberia
- from a little girl writing to her parents in the Congo
- written by a woman to her brother in prison in Kirghizstan
In Columbia, the radio programme Las voces del secuestro broadcasts family messages to people held hostage in the jungle, enabling more than 18,000 people to send news to their loved ones.
In Bagram Prison in Afghanistan, no family visits are allowed, so in 2008 the ICRC and the American authorities developed a videoconferencing system to enable the detainees to communicate with their loved ones.
In the space of just a few months, 70% of the detainees were able to contact their families.

Above: Parwan Detention Facility, Bagram, Afghanistan
And finally the Restoring Family Links exhibition concludes with works by Congolese artist Chuck Ledy and Benin artist Romuald Hazouma.
Humanity has progressed by refusing to accept the inevitability of the phenomena that endanger it.
In the face of natural disasters and epidemics, communities take action to prevent the worst, to save lives and to preserve resources.
Another Chamber of Witnesses:
- Benter Aoko Odhiambo, the head of a Kenyan orphanage and the initiator of a market gardening programme
- Abul Hasnat, a Bangladeshi school teacher and a Red Crescent volunteer
- Madeleen Helmer, the Dutch head of the ICRC Climate Centre
- Jiaqi Kang, a Chinese student in Switzerland
After all, prevention concerns us all.
Blast Theory, a group of British artists, designed the game Hurricane to test the effectiveness of natural disaster preparedness activities.
Planting mangroves, constructing high-level shelters, building up reserve stocks of food and organizing evacuation exercises are all part of the game and involve actors such as ICRC delegates, village leaders, experts and volunteers.
As the hurricane strikes, the players have to evacuate the villagers.
At the end of the game tells us how many lives were saved.
Posters are key communication instruments in prevention initiatives.
The link between pictures and text makes the messages easy for everyone to understand.
The Museum’s collection of some 12,000 posters from more than 120 countries tells of the many different activities developed by the ICRC.
Nowadays, as the impact of global warming becomes clearer, the ICRC is increasingly involved in natural disaster preparedness.
The ICRC was very quick to perceive the role that the cinema could play in promoting its activities.
Some films focused on prevention – hygiene, epidemics and accidents.
Others on training volunteers in first aid or life saving.
While preventing illnesses and accidents is ancient history, the management of risks associated with natural disasters is a more recent development.
A workshop at the Haute école d’art et de design (Gèneve) was given a free hand to create new montages using more than 1,000 films from the Museum’s collection.
Above: Haute école d’art et de design, Genève
Prevention is first and foremost about saving lives.
A number of different measures can be taken to provide protection: building shelters, installing early warning systems, carrying out evacuation exercises and providing hygiene education.
All these activities mobilize the local communities and the humanitarian organizations.
They sometimes call for substantial investment.
It is easy to raise funds during disasters when emotions are running high.
It is more difficult to raise funds for longer-term work.
Nonetheless, one dollar invested in prevention is two to ten dollars saved in emergency relief and reconstruction work.

All of this is brought into sharp focus by the three “théâtres optiques” (Cyclone, Tsunami and Latrines), created for the Museum by the French artist Pierrick Sorin.
Above: Pierrick Sorin
Let’s take, for example, Bangladesh.

Above: Flag of Bangladesh
In 1970, Cyclone Bhola caused one of the worst natural disasters in history.
A 10-metre high wave and winds of 220 km/hour caused the death of 500,000 people here.
A cyclone preparedness programme was then launched, which included an early warning system, the construction of shelters and the training of evacuation volunteers.
In November 2007, Cyclone Sidr, one of the most powerful ever recorded, hit parts of Bengal and Bangladesh, affecting nearly 9 million people and causing vast economic damage.
1.5 million people were evacuated before the Cyclone struck.
Although 3,500 people died, this number of deaths was far below the 1970 disaster.

Or let’s consider Brazil.

Above: Flag of Brazil
Infectious diarrhoea can affect people throughout the world.
It is most frequently caused by water that has been contaminated by faeces.
Around 2 million people die from diarrhoea every year, most of them children in developing countries.
In 2008 more than 2 billion individuals were without suitable latrines.
Almost half of them defecated in the open air.
In 1997, the authorities in Salvador de Bahia in Brazil launched a water purification programme in the city.
A university team monitored 2,000 children under the age of 3, most of whome were living in impoverished urban districts.
The results showed that water purification had a direct impact on health:
The overall number of cases of diarrhoea fell by 22% in the city and by 43% in the poorest areas.

Above: Images of Salvador de Bahia, Brazil
The Museum was never designed with the intention of casting blame or lavishing praise upon particular countries or particular individuals, but rather it shows the situations, both general and particular, in which the ICRC functions and to further a better understanding of what they do.
The ICRC aids victims, not on account of their particular nationality or their particular cause, but purely and simply because they are human beings who are suffering and are in need of help.
It strives to assuage all human distress which has no hope of effective aid from other sources.
The ICRC desires to relieve above all that suffering which is brought about by man, brought about by man’s inhumanity to man, and is more painful on that account and more difficult to relieve.
The most terrible form of man’s inhumanity to man is war and that is why the idea of the Red Cross was born in the field of battle.
The Red Cross is a third front above and across two belligerent fronts, a third front directed against neither of them but for the benefit of both.
The combatants in this third front are interested only in the suffering of the defenceless human being, irrespective of his nationality, his convictions or his past.
The ICRC fights wherever they can against all inhumanity, against every degradation of the human personality, against all injustice directed against the defenceless.
These neutrals on this humanitarian front are free of the prejudice and hostility which is so natural to men engaged in warfare.
The dominant idea and the essence of the Geneva Convention is equality of treatment for all sick and wounded persons whether they are friends or enemies.
It is the fulfilment of the cry of Solferine:
Siamo tutti fratelli.
We are all brothers.
The Museum is a living embodiment of that humanitarian adventure.
It is an edifice of humanity working for humanity.
And it is good.

Sources: Wikipedia / Google / Lonely Planet Switzerland / Rough Guide to Switzerland / Red Cross Museum, The Humanitarian Adventure / The International Committee of the Red Cross, Basic Rules of the Geneva Conventions and their Additional Protocols / Dr. Marcel Junod, Warrior without Weapons




































































































































































































































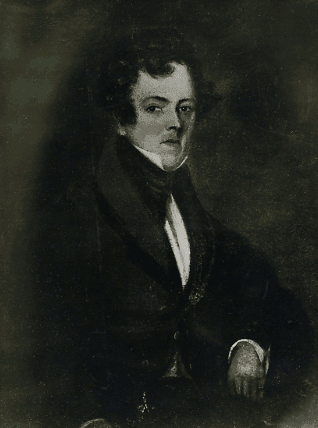







































































































































































































































































































































































![Centered deep red circle on a white rectangle [2]](https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/en/thumb/9/9e/Flag_of_Japan.svg/800px-Flag_of_Japan.svg.png)





































