Landschlacht, Switzerland, Thursday 19 November 2020
A promise made is a debt unpaid.
Since I began blogging (18 May 2015) I have begun a number of consecutive writing projects within these Chronicles of Canada Slim and its companion blog Building Everest.
The select seven subjects that this blog has evolved into following are, accomplished in alphabetical order and covering places previously visited prior to this calendar year in which we find ourselves at this time of writing:
- Alsace (France)
- Italy
- Lanzarote (one of the Canary Islands)
- London (England)
- Porto (Portugal)
- Serbia (Belgrade and Nis)
- Switzerland

I have, since 12 November 2017, written a series of posts, (to be completed in one more Chronicles post after this one), about my adventures and discoveries following a book’s walking itinerary that traces the “footsteps” and life of Swiss reformer Huldrych Zwingli, from his birthplace in the village of Wildhaus to his final resting place in Kappel am Albis.

Above: Huldrych Zwingli (1484 – 1531)
Yvonne and Marcel Steiner, in their book Zwingli-Wege: Zu Fuss von Wildhaus nach Kappel am Albis – Ein Wander- und Lesebuch, break Zwingli’s life progression within Switzerland into nine separate walks.
I have expanded my accounts of Zwingli’s life to include locales off the Steiners’ beaten path (Basel and Vienna) as well as Geneva, the home of the Reformation Museum.

Please see Canada Slim and…..
- the Road to Reformation (12 November 2017)
- the Wild Child of Toggenburg (20 November 2017)
- the Thundering Hollows (27 November 2017)
- the Basel Butterfly Effect (3 December 2017)
- the Vienna Waltz (9 December 2017)
- the Battle for Switzerland’s Soul (18 December 2017)
- the Monks of the Dark Forest (8 January 2018)
- the Privileged Place (26 January 2018)
- the Lakeside Pilgrimage (24 April 2018)
…. of this blog, though Zwingli’s name has popped up in other posts of 2016.

As 2020 is drawing closer to its conclusion (thankfully) and 2021 is on the horizon with plans to relocate to Turkey (depending on corona conditions), I feel compelled in the few months (or weeks) remaining to bring to a conclusion the chronicles begun on the aforementioned seven sites visited prior to 2020, as many of the materials I presently use to compile these accounts may not be available to me once I am settled in Eskisehir.

Above: One of Eskişehir’s many bridges across the Porsuk River
I have also begun to consider whether it has been wise to write about these sites by hopping from one to another in an alphabetical succession of seven, as readers may find it difficult to keep the thread of each narrative clear in their minds.
Thus, it is my intention to immediately follow this post with other Zwingli Way posts until the tale has been told in its totality.
It is my hope, within this blog, during these next two months, to complete many of the tales of the other six sites before Turkey.
It is also my hope, before 2021, to explore and describe more of Switzerland in my companion blog, Building Everest.

Above: Mount Everest
A reform movement is a type of social movement that aims to bring a social or political closer to the community’s ideal.
A reform movement is distinguished from more radical social movements, such as revolutionary movements which reject those old ideals, in that the ideas are often grounded in liberalism, although they may be rooted in socialist (specifically, social democratic) or religious concepts.
Some rely on personal transformation.
Others rely on small collectives, such as Mahatma Gandhi’s spinning wheel and the self-sustaining village economy, as a mode of social change.
Reactionary movements, which can arise against any of these, attempt to put things back the way they were before any successes the new reform movement(s) enjoyed, or to prevent any such successes.

Above: Mohandas Karamchand Gandhi (1869 – 1948), also known as Mahatma Gandhi, was an Indian lawyer, anti-colonial nationalist and political ethicist, who employed nonviolent resistance to lead the successful campaign for India’s independence from British rule, and in turn inspired movements for civil rights and freedom across the world.
The honourific Mahatma (Sanskrit: “great-souled” / “venerable“), first applied to him in 1914 in South Africa, is now used throughout the world.
With his book Hind Swaraj (1909) Gandhi, aged 40, declared that British rule was established in India with the co-operation of Indians and had survived only because of this co-operation.
If Indians refused to co-operate, British rule would collapse and swaraj (home rule) would come.
In February 1919, Gandhi cautioned the Viceroy of India with a cable communication that if the British were to pass the Rowlatt Act, he would appeal to Indians to start civil disobedience.
The British government ignored him and passed the law, stating it would not yield to threats.
The satyagraha (civil disobedience) followed, with people assembling to protest the Rowlatt Act.
On 30 March 1919, British law officers opened fire on an assembly of unarmed people, peacefully gathered, participating in satyagraha in Delhi.

(The Anarchical and Revolutionary Crimes Act of 1919, popularly known as the Rowlatt Act, was a legislative council act passed by the Imperial Legislative Council in Delhi on 18 March 1919, indefinitely extending the emergency measures of preventive indefinite detention, incarceration without trial and judicial review enacted in the 1915 Defence of India Act during the First World War.
It was enacted in light of a perceived threat from revolutionary nationalists to organisations of re-engaging in similar conspiracies as during the War which the Government felt the lapse of the Defence of India Act would enable.)

Above: Sidney Rowlatt (1862 – 1945), best remembered for his controversial presidency of the Rowlatt Committee, a sedition committee appointed in 1919 by the British Indian Government to evaluate the links between political terrorism in India.
People rioted in retaliation.
On 6 April 1919, a Hindu festival day, Gandhi asked a crowd to remember not to injure or kill British people, but to express their frustration with peace, to boycott British goods and burn any British clothing they owned.
He emphasised the use of non-violence to the British and towards each other, even if the other side uses violence.
Communities across India announced plans to gather in greater numbers to protest.
Government warned him to not enter Delhi.
Gandhi defied the order.
On 9 April, Gandhi was arrested.
People rioted.
On 13 April 1919, people including women with children gathered in an Amritsar park, and a British officer named Reginald Dyer (1864 – 1927) surrounded them and ordered his troops to fire on them.

Above: Reginald Dyer, “the butcher of Amritsar“
The resulting Jallianwala Bagh massacre (or Amritsar massacre) of hundreds of Sikh and Hindu civilians enraged the subcontinent, but was cheered by some Britons and parts of the British media as an appropriate response.

Above: Mural depicting 1919 Amritsar Massacre
Gandhi in Ahmedabad, on the day after the massacre in Amritsar, did not criticise the British and instead criticised his fellow countrymen for not exclusively using love to deal with the hate of the British government.
Gandhi demanded that people stop all violence, stop all property destruction, and he went on fast-to-the-death to pressure Indians to stop their rioting.
The massacre and Gandhi’s non-violent response to it moved many, but also made some Sikhs and Hindus upset that Dyer was getting away with murder.
Investigation committees were formed by the British, which Gandhi asked Indians to boycott.
The unfolding events, the massacre and the British response, led Gandhi to the belief that Indians will never get a fair equal treatment under British rulers, and he shifted his attention to swaraj for India.
In 1921, Gandhi was the leader of the Indian National Congress.
He reorganised the Congress.
With Congress now behind him, and Muslim support triggered by his backing the Khilafat movement to restore the Caliph in Turkey, Gandhi had the political support and the attention of the British Raj.

Above: Gandhi with Dr. Annie Besant en route to a meeting in Madras in September 1921.
Earlier, in Madurai, on 21 September 1921, Gandhi had adopted the loincloth for the first time as a symbol of his identification with India’s poor.
(Annie Besant was a British socialist, theosophist, women’s rights activist, writer, orator, educationist and philanthropist.
Regarded as a champion of human freedom, she was an ardent supporter of both Irish and Indian self-rule.
She was a prolific author with over 300 books and pamphlets to her credit.
As an educationist, her contributions included being one of the founders of the Banaras Hindu University.)

Above: Annie Besant (néeWood) (1847 – 1933)
Gandhi expanded his nonviolent non-co-operation platform to include swadeshi – the boycott of foreign-made goods, especially British goods.
Linked to this was his advocacy that khadi (homespun cloth) be worn by all Indians instead of British-made textiles.
Gandhi exhorted Indian men and women, rich or poor, to spend time each day spinning khadi in support of the independence movement.
In addition to boycotting British products, Gandhi urged the people to boycott British institutions and law courts, to resign from government employment, and to forsake British titles and honours.
Gandhi thus began his journey aimed at crippling the British India government economically, politically and administratively.

Above: Gandhi spinning yarn, in the late 1920s
The idea of a reform movement and the Reformation are often confused with each other.
It is important to make a distinction between them, for I wish there to be no identifying as similar the actions of religious reformer Huldrych Zwingli with those of political reformer Mahatma Gandhi.
Though Zwingli and Gandhi both fought for that in which they believed, how they “fought” differed greatly.
The Reformation (alternatively named the Protestant Reformation or the European Reformation) was a major movement within Western Christianity in 16th-century Europe that posed a religious and political challenge to the Catholic Church and in particular to papal authority, arising from what were perceived to be errors, abuses and discrepancies by the Catholic Church.

Above: St. Peter’s Basilica, Vatican City
(The Catholic Church throughout its long history, has on occasion been subject to criticism regarding various beliefs and practices.
Within the Church, this includes differences of opinion regarding the use of Latin at Mass and the subject of clerical celibacy.
In the past, different interpretations of scripture and critiques of clerical laxity and opulence contributed to separations such as the schism with the Eastern Orthodox Church and the Protestant Reformation.
The Catholic Church has also been criticized for its active efforts to influence political decisions, such as the Church’s promotion of the Crusades and its involvement with various 20th century nationalist regimes.
More recent criticism focuses on alleged scandals within the Church, particularly alleged financial corruption and the Catholic Church’s sexual abuse scandals.)

Above: St. Peter’s Basilica, Vatican City
The Reformation was the start of Protestantism and the split of Protestantism from the Roman Catholic Church.

Above: Martin Luther at the Diet of Worms, where he refused to recant his works when asked to by Charles V
The following supply-side factors have been identified as causes of the Reformation:
- The presence of a printing press in a city by 1500 made Protestant adoption by 1600 far more likely.
- Protestant literature was produced at greater levels in cities where media markets were more competitive, making these cities more likely to adopt Protestantism.
- Ottoman incursions decreased, thus allowing conflicts between Protestants and Catholics, helping the Reformation take root.
- Greater political autonomy increased the likelihood that Protestantism would be adopted.
- Where Protestant reformers enjoyed princely patronage, they were much more likely to succeed.
- Proximity to neighbors who adopted Protestantism increased the likelihood of adopting Protestantism.
- Cities that had higher numbers of students enrolled in heterodox (dissident) universities and lower numbers enrolled in orthodox universities were more likely to adopt Protestantism.
The following demand-side factors have been identified as causes of the Reformation:
- Cities with strong cults of saints were less likely to adopt Protestantism.
- Cities where primogeniture – (the right, by law or custom, of the firstborn legitimate child to inherit the parent’s estate in preference to shared inheritance among all or some children, any illegitimate child or any collateral relative) – was practiced were less likely to adopt Protestantism.
- Regions that were poor but had great economic potential and bad political institutions were more likely to adopt Protestantism.
- The presence of bishoprics made the adoption of Protestantism less likely.
- The presence of monasteries made the adoption of Protestantism less likely.
A 2020 study linked the spread of Protestantism to personal ties to Luther (e.g. letter correspondents, visits, former students) and trade routes.

Above: Luther as a friar, with tonsure
The Reformation was a triumph of literacy and the new printing press.
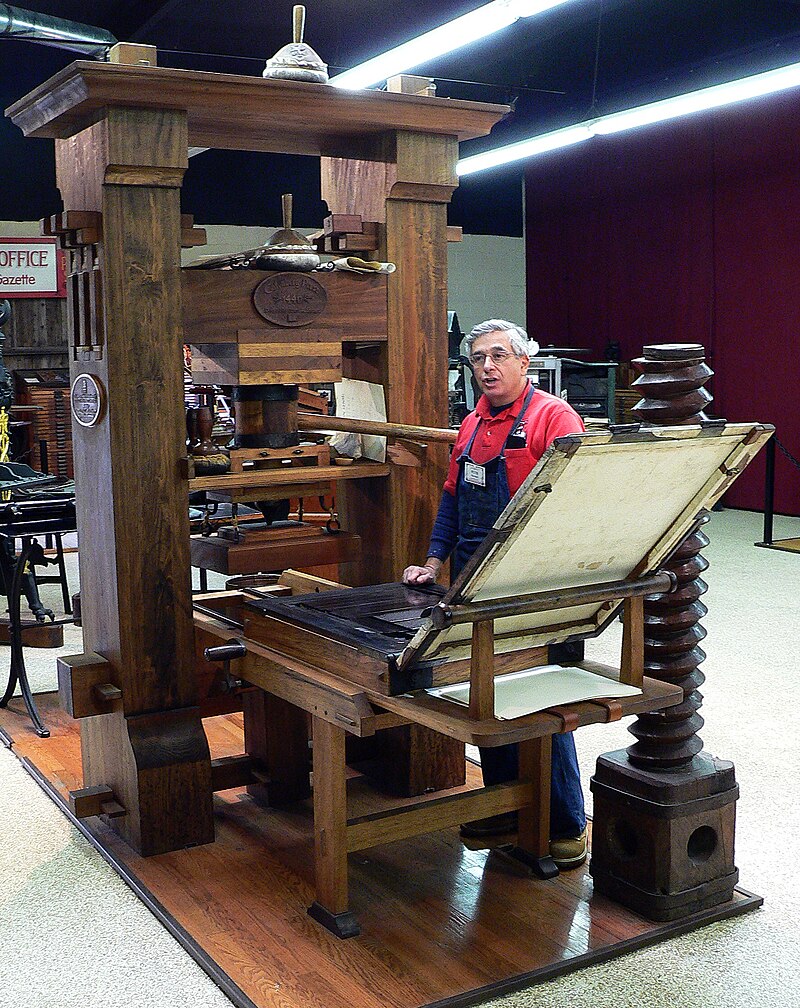

Above: Recreated Gutenberg printing press, International Printing Museum, Carson, California
Luther’s translation of the Bible into German was a decisive moment in the spread of literacy, and stimulated as well the printing and distribution of religious books and pamphlets.
From 1517 onward, religious pamphlets flooded Germany and much of Europe.
By 1530, over 10,000 publications are known, with a total of ten million copies.
The Reformation was thus a media revolution.
Luther strengthened his attacks on Rome by depicting a “good” against “bad” church.
From there, it became clear that print could be used for propaganda in the Reformation for particular agendas, although the term propaganda derives from the Catholic Congregatio de Propaganda Fide (Congregation for Propagating the Faith) from the Counter-Reformation.

Above: The headquarters of the Propaganda fide in Rome
Reform writers used existing styles, cliches and stereotypes which they adapted as needed.
Especially effective were writings in German, including Luther’s translation of the Bible, catechisms for parents teaching their children and for pastors.
Using the German vernacular they expressed the Apostles’ Creed in simpler, more personal, Trinitarian language.
Illustrations in the German Bible and in many tracts popularized Luther’s ideas.

Lucas Cranach the Elder (1472 – 1553), the great painter patronized by the electors of Wittenberg, was a close friend of Luther, and he illustrated Luther’s theology for a popular audience.
He dramatized Luther’s views on the relationship between the Old and New Testaments, while remaining mindful of Luther’s careful distinctions about proper and improper uses of visual imagery.

Above: Lucas Cranach the Elder (1472 – 1553)
Although the Reformation is usually considered to have started with the publication of the Ninety-five Theses by Martin Luther in 1517, there was no schism between the Catholic Church and the nascent Luther until the 1521 Edict of Worms.
The edict condemned Luther and officially banned citizens of the Holy Roman Empire from defending or propagating his ideas.

Above: Martin Luther’s Ninety-five Theses
The end of the Reformation era is disputed:
It could be considered to end with the enactment of the confessions of faith.
Other suggested ending years relate to the Counter-Reformation (1545 – 1648) or the Peace of Westphalia (24 October 1648).
From a Catholic perspective, the Second Vatican Council (11 October 1962 – 8 December 1965) called for an end to the Counter-Reformation.

Above: The historical town hall of Münster where the Peace of Westphalia treaty was signed, ending the Thirty Years’ War (1618 – 1648)
The oldest Protestant churches date their origins to Jan Hus (John Huss) in the early 15th century.
As it was led by a Bohemian noble majority, the Hussite Reformation was Europe’s first “Magisterial Reformation“, because the ruling magistrates supported it, unlike the “Radical Reformation“, which the state did not support.
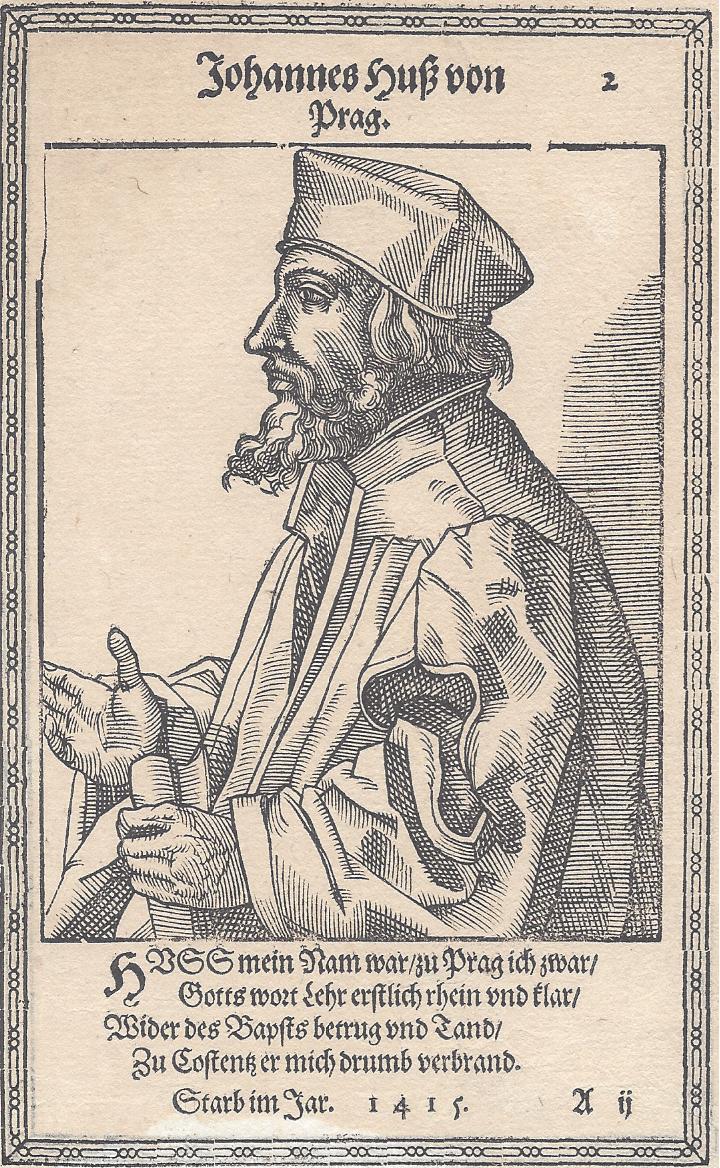

Above: Woodcut of Jan Hus (1372 – 1415)
Common factors that played a role during the Reformation and the Counter-Reformation included the rise of nationalism, simony (the selling of Church offices and relics), the appointment of Cardinal-nephews (a cardinal elevated by a pope who was that cardinal’s relative) and other corruption of the Roman Curia (the administrative body of the Catholic Church) and other ecclesiastical hierarchy, the impact of humanism (a philosophical stance that emphasizes the value and agency of human beings, individually and collectively), the new learning of the Renaissance (15th & 16th centuries) versus scholasticism (learning as interpreted through the Catholic faith), and the Western Schism (a split within the Catholic Church, lasting from 1378 to 1417, in which two men (by 1410 three) simultaneously claimed to be the true Pope, during which each excommunicated the others) that eroded loyalty to the Papacy.

Above: Coat of arms of the Papacy
Unrest due to this Great Schism excited wars between princes, uprisings among the peasants, and widespread concern over corruption in the Church, especially from John Wycliffe at Oxford University and from Jan Hus at Charles University in Prague.

Above: John Wycliffe (1328 – 1384)
Hus objected to some of the practices of the Roman Catholic Church and wanted to return the church in Bohemia and Moravia to earlier practices: liturgy (services) in the language of the people (i.e. Czech), having lay people receive communion (ceremonial breaking of bread and drinking of wine), married priests, and eliminating indulgences (payments buying souls out of Purgatory) and the concept of Purgatory (a between-land between Heaven and Hell).
Some of these, like the use of local language as the liturgical language, were approved by the Pope as early as the 9th century.

The leaders of the Roman Catholic Church condemned Hus at the Council of Constance (Konstanz) (1414–1417) by burning him at the stake despite a promise of safe-conduct.

Above: Execution of Jan Hus, Konstanz
Wycliffe was posthumously condemned as a heretic and his corpse exhumed and burned in 1428.

Above: Burning Wycliffe’s bones, Lutterworth, Leicestershire, England (1428), from Foxe’s Book of Martyrs (1563)
The Council of Constance confirmed and strengthened the traditional medieval conception of church and empire.
The Council did not address the national tensions or the theological tensions stirred up during the previous century and could not prevent schism and the Hussite Wars in Bohemia (1419 – 1434).

Above: Council Hall building, Konstanz, Germany
Pope Sixtus IV (1471–1484) established the practice of selling indulgences to be applied to the dead, thereby establishing a new stream of revenue with agents across Europe.

Above: Pope Sixtus IV (né Francesco della Rovere) (1414 – 1484)
Pope Alexander VI (1492–1503) was one of the most controversial of the Renaissance popes.
He was the father of seven children.

Above: Pope Alexander VI (né Rodrigo de Borja) (1431 – 1503)
In response to papal corruption, particularly the sale of indulgences, Luther wrote The Ninety-Five Theses.

Above: Martin Luther (1483– 1546)
A number of theologians in the Holy Roman Empire preached reformation ideas in the 1510s, shortly before or simultaneously with Luther, including Christop Schappeler in Memmingen (as early as 1513).

Above: Christoph Schappeler (1472 – 1551) was a German religious figure, reformer, and a preacher at St. Martin’s in Memmingen during the early 16th century and during the Protestant Reformation and the German Peasants’ War.
(Schappeler tended to side with the poor, causing the Senate to regulate his sermons in 1516.
However, by 1521 the climate had changed such that the senate was giving him support.
When he was excommunicated in 1524, the Senate refused to follow the bishop’s order to have him banished.
It is believed that Schappeler and Sebastian Lotzer wrote The Twelve Articles: The Just and Fundamental Articles of All the Peasantry and Tenants of Spiritual and Temporal Powers by Whom They Think Themselves Oppressed in early 1525.
Within two months of its initial publication in Memmingen, 25,000 copies of the Twelve Articles had spread throughout Europe.
The Twelve Articles was a religious petition that utilized Luther’s ideas to appeal for peasants’ rights.)

Above: Twelve Articles of the Peasants pamphlet of 1525
The Reformation is usually dated to 31 October 1517 in Wittenberg, Saxony, when Luther sent his Ninety-five Theses on the Power and Efficacy of Indulgences to the Archbishop of Mainz.
The theses debated and criticized the Church and the papacy, but concentrated upon the selling of indulgences and doctrinal policies about Purgatory, particular judgment, and the authority of the pope.
Luther would later write works on devotion to the Virgin Mary, the intercession of and devotion to the saints, the sacraments, mandatory clerical celibacy, and later on the authority of the pope, the ecclesiastical law, censure and excommunication, the role of secular rulers in religious matters, the relationship between Christianity and the law, good works, and monasticism.

Some nuns, such as Katharina von Bora and Ursula of Munsterberg, left the monastic life when they accepted the Reformation, but other orders adopted the Reformation, as Lutherans continue to have monasteries today.
In contrast, Reformed areas typically secularized monastic property.
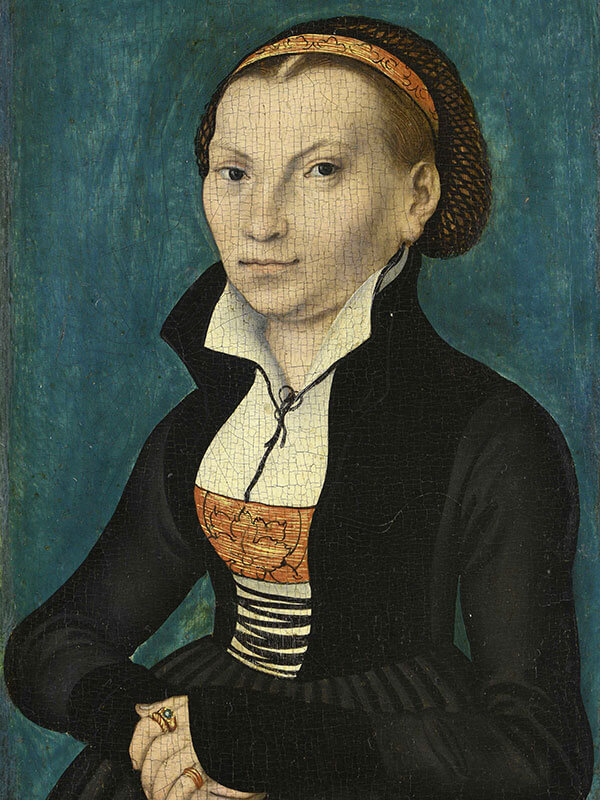

Above: Katharina von Bora, “the Lutheress” (1499 – 1552)
Reformers and their opponents made heavy use of inexpensive pamphlets as well as vernacular Bibles using the relatively new printing press, so there was swift movement of both ideas and documents.
Magdalena Heymair printed pedagogical writings for teaching children Bible stories.

Parallel to events in Germany, a movement began in Switzerland under the leadership of Huldrych Zwingli.
These two movements quickly agreed on most issues, but some unresolved differences kept them separate.
Some followers of Zwingli believed that the Reformation was too conservative, and moved independently toward more radical positions, some of which survive among modern day Anabaptists.

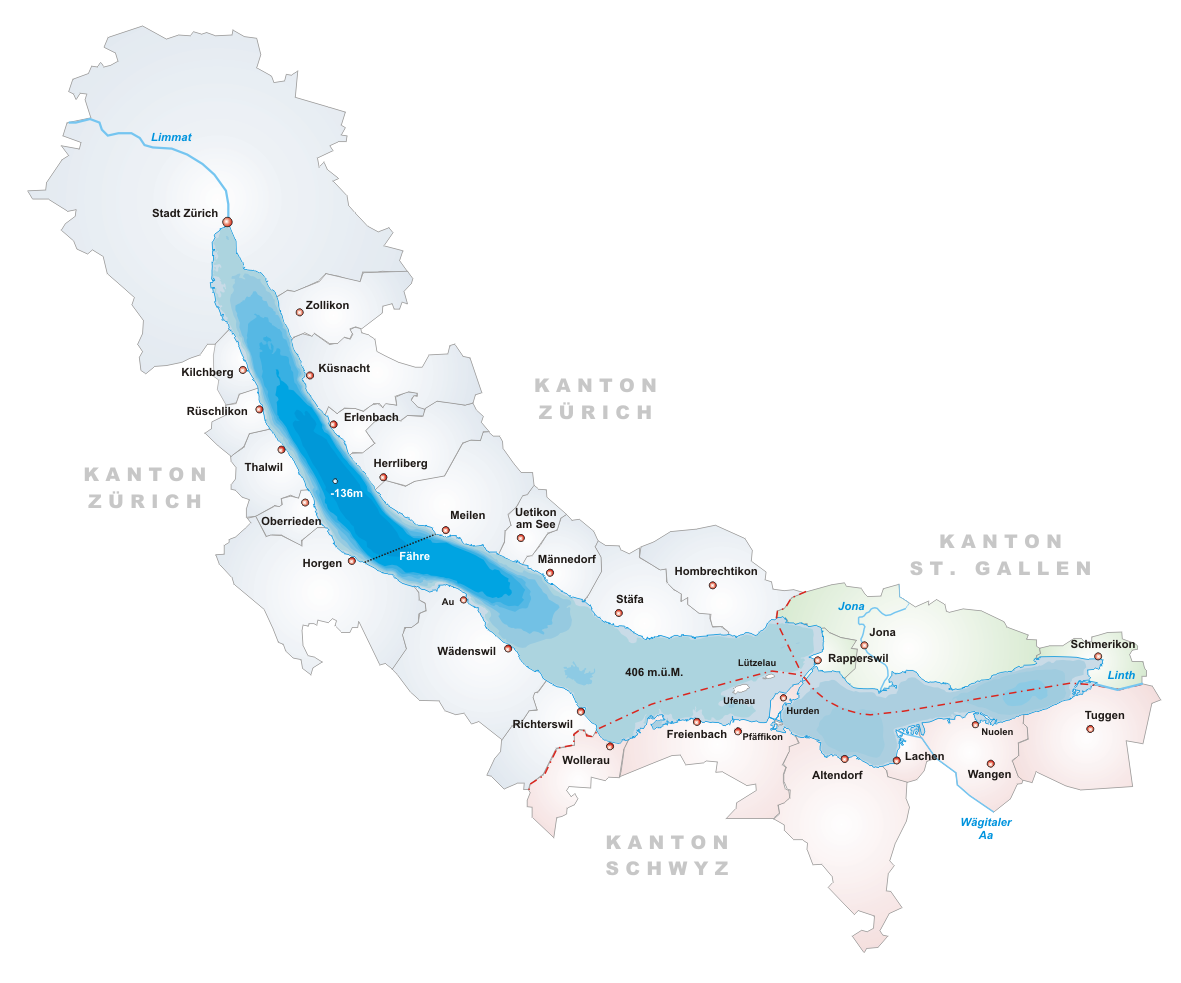
Above: The Grossmünster (large cathedral) in the centre of the medieval town of Zürich (Murer map, 1576)
After this first stage of the Reformation, following the excommunication of Luther in Decet Romanum Pontificum and the condemnation of his followers by the edicts of the 1521 Diet of Worms, the work and writings of John Calvin were influential in establishing a loose consensus among various churches in Switzerland, Scotland, Hungary, Germany and elsewhere.

Above: the Decet Romanum Pontificem
Although the German Peasants’ War (1524 – 1525) began as a tax and anti-corruption protest as reflected in the Twelve Articles, its leader Thomas Müntzer gave it a radical Reformation character.
It swept through the Bavarian, Thurginian and Swabian principalities in the general outrage against the Catholic hierarchy.
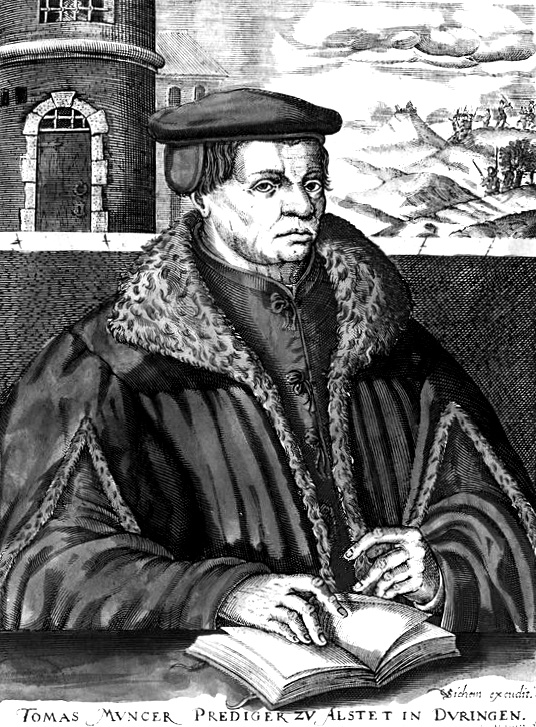

Above: Thomas Müntzer (1489 – 1525)
In response to reports about the destruction and violence, Luther condemned the revolt in writings, such as Against the Murderous Thieving Hordes of Peasants.
Zwingli and Luther’s ally Phillip Melanchthon also did not condone the uprising.
Some 100,000 peasants were killed by the end of the war.

Above: Philipp Melanchthon (né Schwartzerdt) (1497 – 1560)
The city of Zürich, then mainly dominated by the ancient families of Zürich and the guild representatives in the Kleiner Rat (the executive) and Grosser Rat – after about the 1490s mainly an equivalent of present-day committees to assist – supported in the late European Middle Ages the then popular mendicant (religious) orders by attributing them free plots in the suburbs and asked to support the construction of the city wall in return, and the city’s fortification those construction began in the late 11th or 12th century and further on.
Fraumünster Abbey was established in 873 and its abbesses were imperial representans, that is, they were de facto the mistresses of the city republic of Zürich to 1524.

Above: Fraumünster Abbey, Zürich
Memorial measurements in Zürich usually had to be held until the 14th century at Grossmünster, because thus the most income was achieved.
Until the Reformation in Switzerland, all income obtained with the funerals had also to be delivered to the main parish church.

Above: Grossmünster, Zürich
Within the City, the mendicant orders, namely the Predigerkloster and the Augustinerkloster in the 15th-century had been reduced to the function of area pastors, thus the orders supported regime of the Guilds of Zürich.

Above: Predigerkirche, Zürich

Above: Augustinerkirche, Zürich
The priories at Grossmünster and St. Peter were responsible for all religion related questions and decisions.

Above: St. Peter Church, Zürich
The Oetenbach nunnery (1321) became influential, as well as the convent of the Fraumünster had for centuries, as also its nuns came from noble families, and therefore the women monasteries in fact were influential, just by the fact that they owned the most financial resources and estates in the so-called Zürichgau.
These were leased to the peasant population, and they had to bring their products to feed Zürich.
Furthermore, the water mills and the coinage right were held by the Fraumünster Abbey.
More or less influence had the merchants that primarily secured the long distance trade outside the Old Swiss Confederacy, and later the Guilds, but rather as member of the Grosser Rat, and their 12 deans in the Kleiner Rat in the 14th and 15th century.

Above: The area of the abolished nunnery towards Uraniastrasse, as seen from Limmatquai, Schipfe and Lindenhof to the left, with the Waisenhaus building to the right.
Zwingli was born during a time of emerging Swiss patriotism and increasing criticism of the Swiss mercenary.
He attended the University of Vienna and the University of Basel, a scholarly center of Renaissance humanism.

Above: Logo of the University of Vienna

Above: Logo of the University of Basel
Zwingli continued his studies while he served as a pastor in Glaurus and later in Einsiedeln, where he was influenced by the writings of Erasmus.

Above: Glarus Cathedral

Above: Einsiedeln Abbey
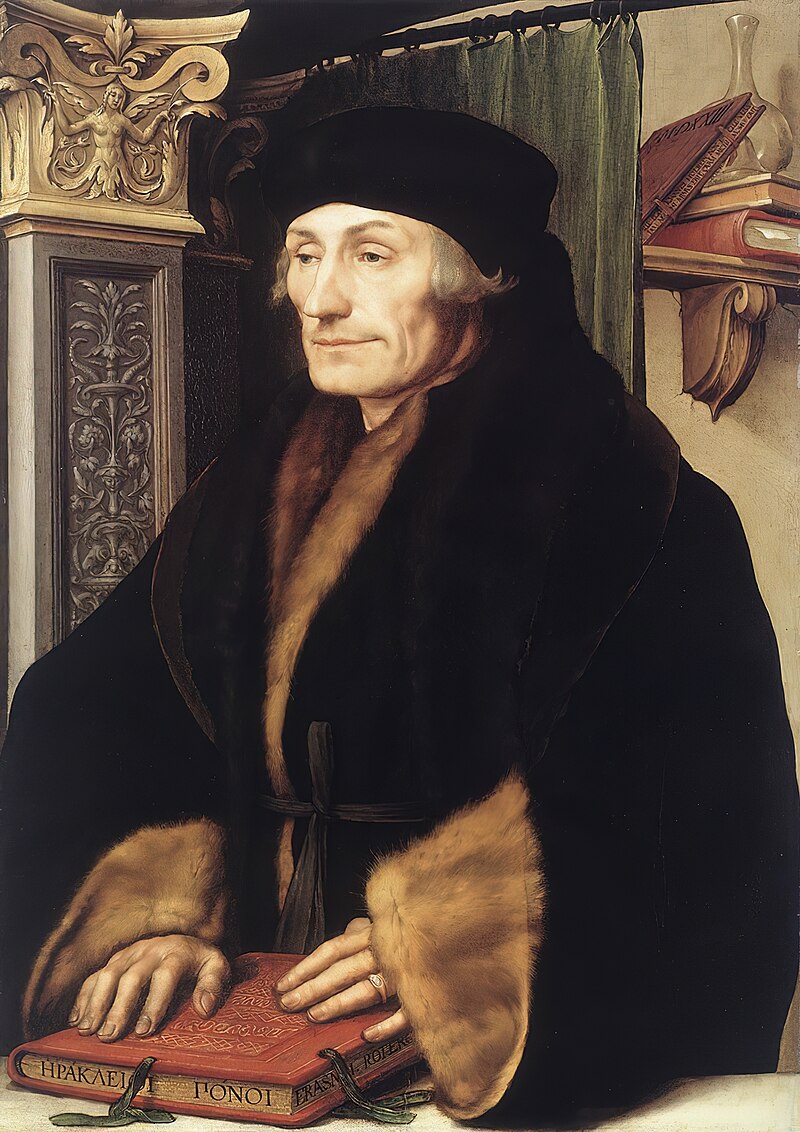

Above: Desiderius Erasmus of Rotterdam (1469 – 1536)
Congratulations!
You have read a lot and you (hopefully) have learned a lot up to this point.
You learned of my motivations.
You learned the distinction between a reform movement and a reformation.
You are beginning to see the context and background of the events that led to Zwingli’s journey to Zürich.
The problem now for you, gentle readers, is to someone connect these events of the past and somehow relate them to today’s reality.
Zürich, and of course the aforementioned Steiners’ guidebook, recommend a walking tour of the city as seen through the eyes of Zwingli and the events of the Reformation.
(Contatc the Zürich Tourism Board – http://www.zuerich.com – for more information and guided tours – http://www.zwingli.ch.)
In 1519, Zwingli became the Leutpriester (people’s priest) of the Grossmünster in Zürich where he began to preach ideas on reform of the Catholic Church.
On 1 January 1519, Zwingli gave his first sermon in Zürich.
Deviating from the prevalent practice of basing a sermon on the Gospel lesson of a particular Sunday, Zwingli, using Erasmus’ New Testament as a guide, began to read through the Gospel of Matthew, giving his interpretation during the sermon, known as the method of lectio continua.
He continued to read and interpret the book on subsequent Sundays until he reached the end and then proceeded in the same manner with the Acts of the Apostles, the New Testament epistles, and finally the Old Testament.
His motives for doing this are not clear, but in his sermons he used exhortation to achieve moral and ecclesiastical improvement which were goals comparable with Erasmian reform.
Sometime after 1520, Zwingli’s theological model began to evolve into an idiosyncratic form that was neither Erasmian nor Lutheran.

Scholars do not agree on the process of how he developed his own unique model.
One view is that Zwingli was trained as an Erasmian humanist and Luther played a decisive role in changing his theology.
Another view is that Zwingli did not pay much attention to Luther’s theology and in fact he considered it as part of the humanist reform movement.
A third view is that Zwingli was not a complete follower of Erasmus, but had diverged from him as early as 1516 and that he independently developed his own theology.

Above: Entrance to the Grossmünster doors is inscribed Matthew 11:28: “Come to me, all who labor and are heavy laden, and I will give you rest.“
Zwingli’s theological stance was gradually revealed through his sermons.
He attacked moral corruption and in the process he named individuals who were the targets of his denunciations.
Monks were accused of indolence and high living.
In 1519, Zwingli specifically rejected the veneration (worship) of saints and called for the need to distinguish between their true and fictional accounts.

Zwingli cast doubts on hellfire, asserted that unbaptised children were not damned, and questioned the power of excommunication – to deprive, suspend, or limit membership in a religious community or to restrict certain rights within it, in particular, those of being in communion with other members of the congregation, and of receiving the Sacraments (baptism, confirmation, the Eucharist (communion), penance (confession), anointing of the sick, Holy Orders (devoting one’s life to the Church) and matrimony.)
His attack on the claim that tithing was a divine institution, however, had the greatest theological and social impact.
This contradicted the immediate economic interests of the foundation.

Above: The Seven Sacraments, altarpiece by Rogier van der Weyden, 1448
One of the elderly canons who had supported Zwingli’s election, Konrad Hofmann, complained about his sermons in a letter.
Some canons supported Hofmann, but the opposition never grew very large.
Zwingli insisted that he was not an innovator and that the sole basis of his teachings was Scripture.

Within the Diocese of Konstanz, Bernhardin Sanson was offering a special indulgence for contributors to the building of St. Peter’s in Rome.
When Sanson arrived at the gates of Zürich at the end of January 1519, parishioners prompted Zwingli with questions.
Zwingli responded with displeasure that the people were not being properly informed about the conditions of the indulgence and were being induced to part with their money on false pretences.
This was over a year after Martin Luther had published his 95 Theses on 31 October 1517.
The council of Zürich refused Sanson entry into the city.
As the authorities in Rome were anxious to contain the fire started by Luther, the Bishop of Konstanz denied any support of Sanson and he was recalled.

Above: Inscription, St. John Lateran, Rome:
Indulgentia plenaria perpetua quotidiana toties quoties pro vivis et defunctis
(“Perpetual everyday plenary indulgence on every occasion for the living and the dead“)
Our tour through Reformation-time Zurich takes us to the important
places in Reformer Zwingli’s life and in those of his successors.
The Reformation movement radically changed the Zurich area and the whole Swiss Confederation.
Unlike Germany, where rulers determined the policies of the
Church, Switzerland’s system featured pre-democratic structures,
which influenced the Reformation movement.
When Ulrich Zwingli was appointed Leutpriester (Priest
in charge of the local parish and pilgrims) at Grossmünster Cathedral by the Council of Zürich, he reported his activities to the government of Zürich.

As previously mentioned Zwingli had been a priest at Einsiedeln.
As a military chaplain he had witnessed the Battle of Marignano in 1515, in
which approximately 10,000 Swiss mercenaries, including many child soldiers, were killed.
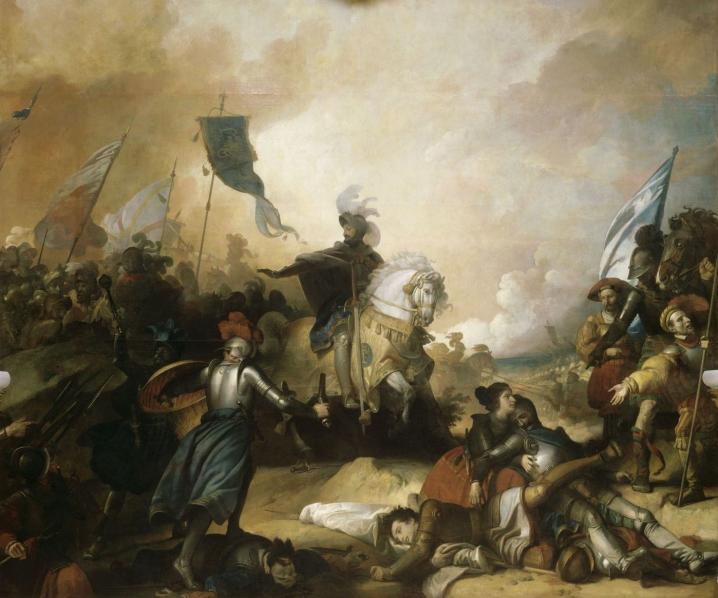

Above: Francis I (1494 – 1547) Orders His Troops to Stop Pursuing the Swiss at the Battle of Marignano (13 – 14 September 1515)
From the very beginning of his ministry in Zürich, Zwingli criticized
the lucrative mercenary business, the worship of saints, the selling of
indulgences and the mass.

Above: A member of the Pontifical Swiss Guard with halberd (2011)
Zwingli’s arguments against the religious practices of his day were based on
the Bible.
From day one, instead of delivering his sermons on the prescribed church lectionary readings, he began preaching the Gospel of Matthew from beginning to end.
Zwingli soon found sympathizers, like-minded theologians, but also citizens and members of the government.
He stayed in contact with other localities within the Swiss Confederation, where the ideas of the Reformation were also attracting attention.

Above: Map of Switzerland, 1530
Today’s Grossmünster was largely built between 1100 and 1250.
It served equally as parish church and as a convent for the canons.
The Grossmünster was a monastery church, vying for precedence with the Fraumünster across the Limmat throughout the Middle Ages.
According to legend, the Grossmünster was founded by Charlemagne (748 – 814), whose horse fell to its knees over the tombs of Felix and Regula, Zürich’s patron saints.

Above: Charlemagne on the bronze doors
The legend helps support a claim of seniority over the Fraumünster, which was founded by Louis the German (806 – 876), Charlemagne’s grandson.

Above: Seal with Louis’ inscription and effigy
Recent archaeological evidence confirms the presence of a Roman burial ground at the site.
![The Roman Empire in 117 AD at its greatest extent, at the time of Trajan's death (with its vassals in pink)[3]](https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/0/00/Roman_Empire_Trajan_117AD.png/1920px-Roman_Empire_Trajan_117AD.png)
Above: The Roman Empire at its greatest extent
Felix and Regula were siblings and members of the Theban Legion (an entire Roman legion of 6,666 men who had converted en masse to Christianity and were martyred together in 286) under St. Maurice (d. 287), stationed in Aguanum (modern St. Maurice) in the Valais (southwestern Switzerland).

Above: St. Maurice (left)

Above: St. Maurice
When the Legion was to be executed in 286, Felix and Regula fled, reaching Zürich before they were caught, tried and executed.
After decapitation, they miraculously stood to their feet, picked up their own heads, walked forty paces uphill, and prayed before lying down in death.

They were buried on the spot where they lay down, on the hilltop which would become the site of the Grossmünster.

Above: The Murer map, 1576.
Shown is the Grossmünster, burial place of Saints Felix and Regula at the river Limmat, the Wasserkirche (Water Church), their execution site, and, on the left side of the Limmat, the Fraumünster Abbey, where important relics of the saints used to be on display to the public.
Their story was revealed in a dream to a monk called Florentius.

Above: Jesus and the patron saints of Zürich – Felix, Regula and Exuperantius
This story largely contributed to the massive conversion of the inhabitants of these regions to Christianity and had such an impact on Zürich that these three saints still appear on the seal of Zürich today.
In the 9th century, there was a small monastery at the location, outside the settlement of Zürich which was situated on the left side of the Limmat.
The Grossmünster was built on their graves from 1100.
From the 13th century, images of the saints were used in official seals of the city and on coins.
On the saints’ feast day, their relics were carried in procession between the Grossmünster and the Fraumünster, and the two monasteries vied for possession of the relics, which attracted enough pilgrims to make Zürich the most important pilgrimage site in the bishopric of Konstanz.

Above: Konstanz Cathedral
The Knabenschiessen (a traditional target shooting competition held on the 2nd weekend of September each year) of Zürich originates with the feast day of the saints on 11 September, which came to be the “national holiday” of the early modern Republic of Zürich.

Above: Coat of arms of Zürich
(The Knabenschiessen competition is open to 13- to 17-year-olds who either reside or are enrolled in a school in the canton of Zürich.
Originally reserved for boys (Knaben), the competition has been open to female participants since 1991.
The shooting is with the Swiss Army ordinance rifle, SIG SG 550.
The competition is held in the shooting range at Albisgütli to the southwest of the city center, on the slope of Uetliberg.
It is surrounded by a large fair.)

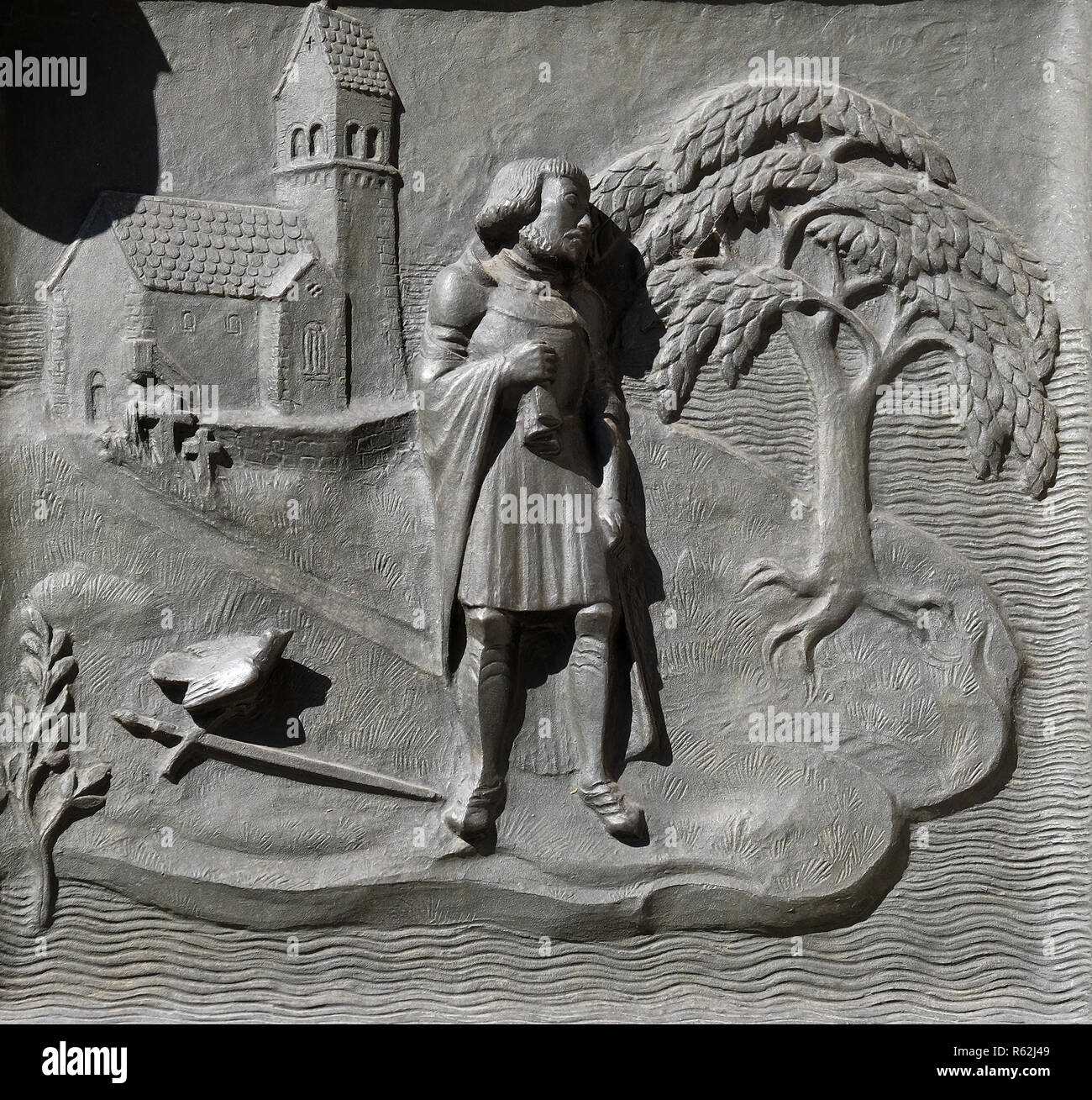
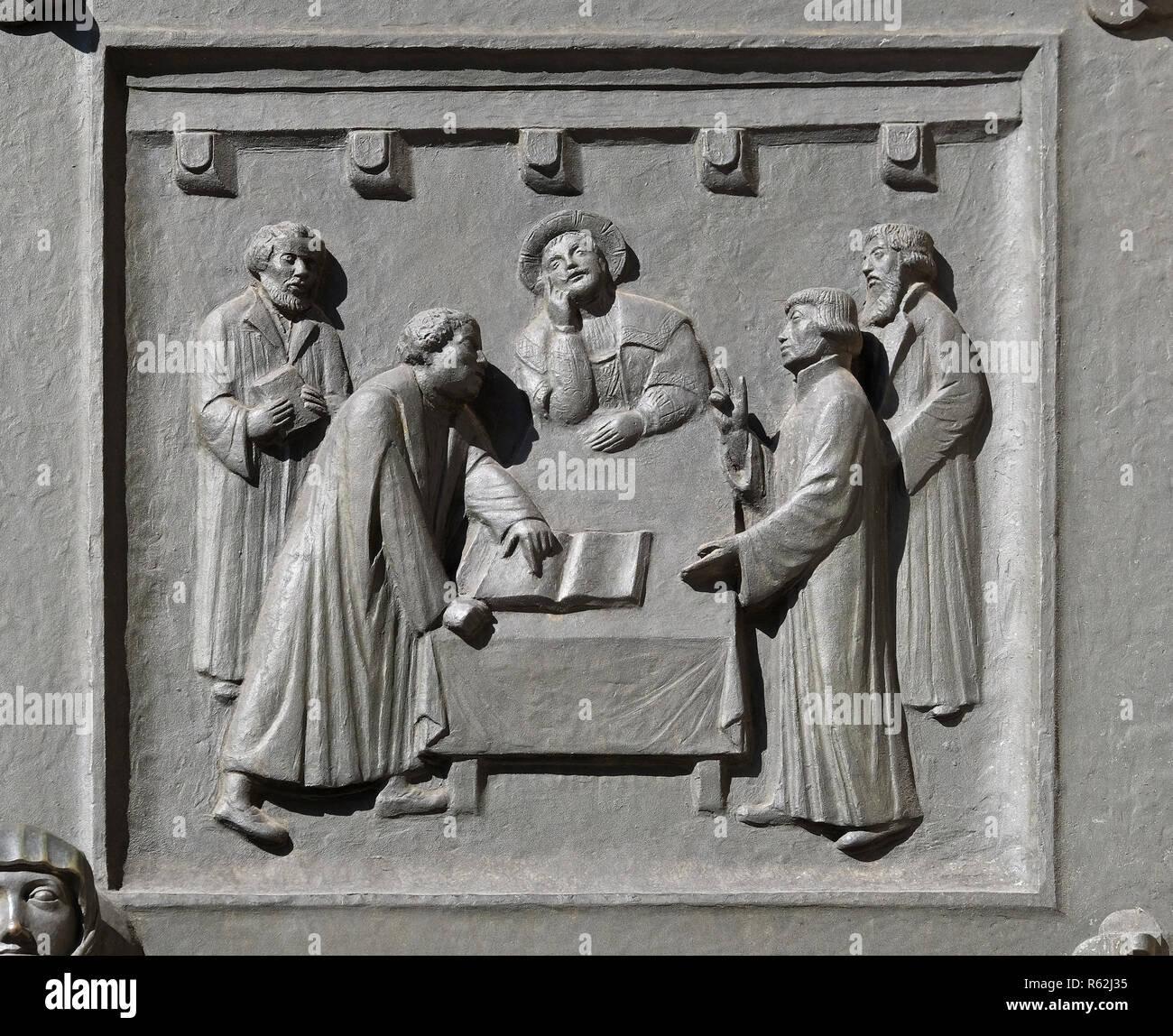
The Grossmünster is, in my opinion, the best site to start a Reformation Tour of Zürich, for its door, a bronze portal, a creation of the sculptor Otto Münch in 1939, depicts 16 scenes of Zwingli’s life.
Starting from the lower left side:
The second plate depicts the 14 year-old Zwingli playing his lute as a pupil of the Bern Dominicans.
It then shows him as a military chaplain preaching to the soldiers before the Battle of Marignano in 1515.
On the second row from the bottom to the far right we see the first celebration of the Lord’s Supper after mass had been abolished.
Further up Zwingli can be seen with his family and then translating the Bible.
The knight Ulrich von Hutten is pictured on the next plate.
Zwingli granted him asylum on Ufenau Island to save him from persecution by the German Empire.
Further up on the left the “Mushafen” (a large pot of mush) scene shows the feeding of the poor next to the Preacher‘s Church.

On the same row to the right a plate illustrates the Marburg Disputation, where Luther and Zwingli haggled over the meaning of the Lord’s Supper in
1529, but could not reach common ground.
Not until 1973 were the Leuenberg Agreements signed by the Churches of Europe and the differences resolved.

The square directly above this depicts Zwingli’s death near Kappel on 11 October 1531.
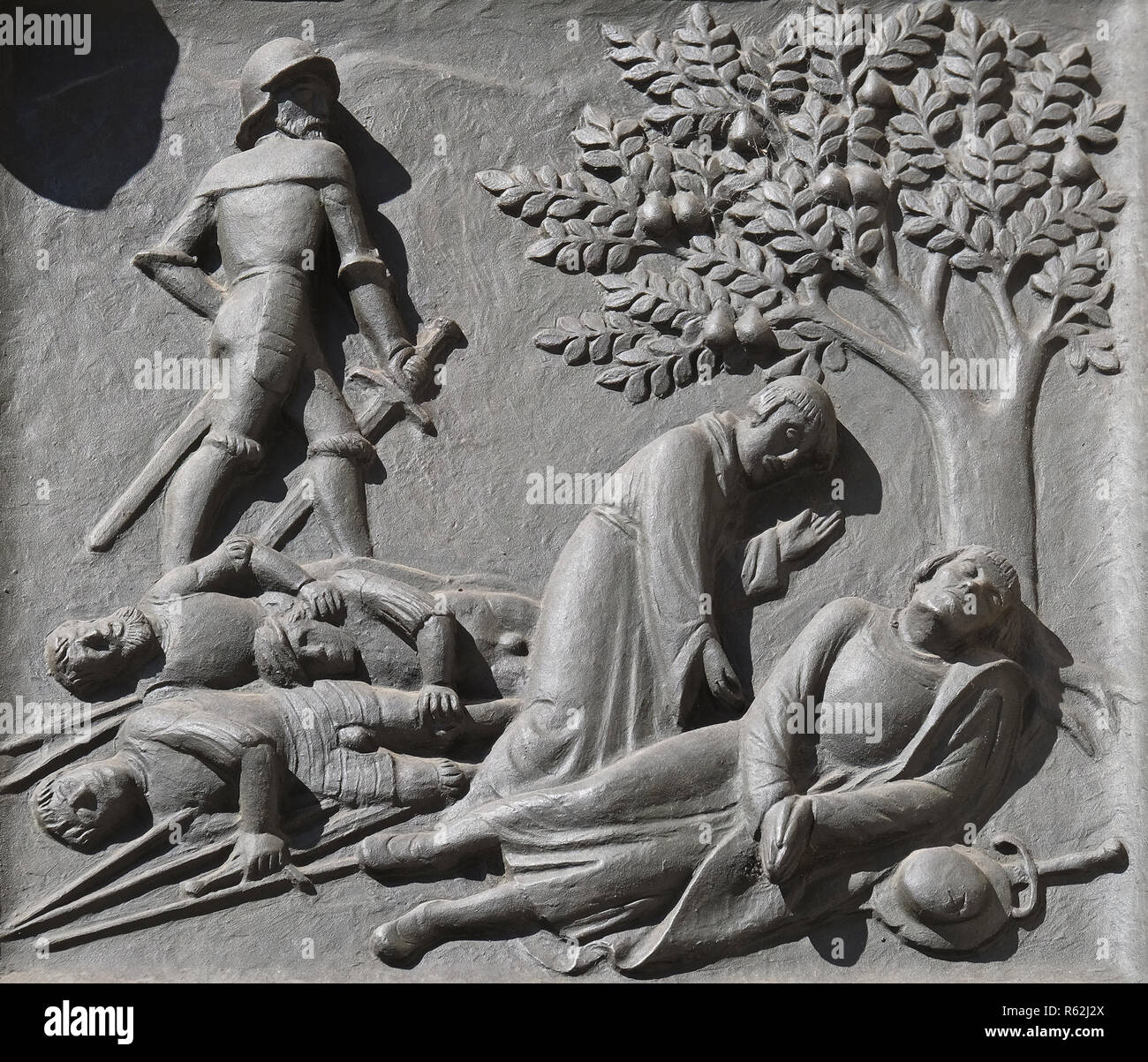

There are also illustrations showing Zwingli’s successor Heinrich Bullinger and Reformers from other Swiss cities.

Zurich had 7,000 inhabitants at the time of the Reformation.
This figure was reduced to 5,000 following an outbreak of the black plague.
In August 1519, Zürich was struck by an outbreak of the Black Plague during which at least one in four persons died.
All of those who could afford it left the city, but Zwingli remained and continued his pastoral duties.
In September, he caught the disease and nearly died.
He described his preparation for death in a poem, Zwingli’s Pestlied (plague song) consisting of three parts: the onset of the illness, the closeness to death, and the joy of recovery.
The final verses of the first part read (translated):
“Thy purpose fulfil.
Nothing can be too severe for me.
I am Thy vessel for You to make whole or break into pieces.
Since, if You take hence my spirit from this earth, You do it so that it will not grow evil and will not mar the pious lives of others.“

In his first public controversy in 1522, he attacked the custom of fasting during Lent.
(Lent is a solemn religious observance in the Christian liturgical calendar that begins on Ash Wednesday and ends approximately six weeks later, before Easter Sunday.
The purpose of Lent is the preparation of the believer for Easter through prayer, doing penance, mortifying the flesh, repentence of sins, almsgiving and self-denial.)

On the first fasting Sunday, 9 March, Zwingli and about a dozen other participants consciously transgressed the fasting rule by cutting and distributing two smoked sausages (the Wurstessen – sausage meal – in Christoph Froschauer’s print workshop).


Above: Christoph Froschauer (1490 – 1564)
Zwingli defended this act in a sermon which was published on 16 April, under the title Von Erkiesen und Freiheit der Speisen (Regarding the Choice and Freedom of Foods).
He noted that no general valid rule on food can be derived from the Bible and that to transgress such a rule is not a sin.
The event, which came to be referred to as the Affair of the Sausages, is considered to be the start of the Reformation in Switzerland.

Above: The Froschau quarter in Zürich, as shown on the 1576 Murer map, printed by Christoph Froschauer
According to William Roscoe Estep, Zwingli had already held his convictions for some time before the incident.
In March 1522, he was invited to partake of the sausage supper that Froschauer served not only to his workers, who, as he later claimed, were exhausted from putting out the new edition of the Epistles of St. Paul, but also to various dignitaries and priests.
Because the eating of meat during Lent was prohibited, the event caused public outcry, which led to Froschauer being arrested.
The planned provocation took place in the presence of Leo Jud, Klaus Hottinger and Lorenz Hochrütiner, which all gained notoriety for Swiss reformation later.

Above: Leo Jud (1482 – 1542)

Above: Klaus Hottinger (d. 1524)
Froschauer himself published the Zürich Bible.

Above: the Zürich Bible – It is thought to be the first Bible to contain a map.
The meal involved Swiss Fasnachtskiechli and some slices of sharp smoked hard sausage, which had been stored for more than a year.
Though he himself did not eat the sausages, Zwingli was quick to defend Froschauer from allegations of heresy.
In his Von Erkiesen und Freiheit der Speisen sermon, Zwingli argued that fasting should be entirely voluntary, not mandatory.

Above: Home of Christoph Froschauer, Brunngasse 18, Zürich
According to Michael Reeves, Zwingli was advancing the Reformation position that Lent was subject to individual rule, rather than the discipline which was upheld at the time by the Catholic Church.
However the Zürich sausage affair was interpreted as a demonstration of Christian liberty and of similar importance for Switzerland as Martin Luther’s 95 Theses were for German reformation.

After hearing of this indictment, Hugo Hohenlandenberg, the Bishop of Konstanz, was so scandalized by Zwingli’s preaching that he called for a mandate prohibiting the preaching of any Reformation doctrine in Switzerland.
However, the damage had already been done, and Zwingli went on to become an extremely popular and revered figure in Swiss Protestantism, having contracted and recovered from the Black Plague and drawn up 67 theses (similar to Martin Luther’s 95 theses) that denounced several long-standing beliefs of the Church of Rome.

Above: Hugo von Hohenlandenberg (1457 – 1532)
Following this event, Zwingli and other humanist friends petitioned the bishop on 2 July to abolish the requirement of celibacy on the clergy.
Two weeks later the petition was reprinted for the public in German as Eine freundliche Bitte und Ermahnung an die Eidgenossen (A Friendly Petition and Admonition to the Confederation).
The issue was not just an abstract problem for Zwingli, as he had secretly married a widow, Anna Reinhart, earlier in the year.
Their cohabitation was well-known and their public wedding took place on 2 April 1524, three months before the birth of their first child.
They would eventually have four children: Regula, William, Huldrych, and Anna.

Above: Remembrance plaque, Schifflände 30
As the petition was addressed to the secular authorities, the bishop responded at the same level by notifying the Zürich government to maintain the ecclesiastical order.
Other Swiss clergymen joined in Zwingli’s cause which encouraged him to make his first major statement of faith, Apologeticus Archeteles (The First and Last Word).
He defended himself against charges of inciting unrest and heresy.
He denied the ecclesiastical hierarchy any right to judge on matters of church order because of its corrupted state.
The events of 1522 brought no clarification on the issues.
Not only did the unrest between Zürich and the bishop continue, tensions were growing among Zürich’s Confederation partners in the Swiss Diet (national council).
On 22 December, the Diet recommended that its members prohibit the new teachings, a strong indictment directed at Zürich.
The City Council felt obliged to take the initiative and find its own solution.

Above: Federal Diet of Switzerland, 1531
On 3 January 1523, the Zürich City Council invited the clergy of the city and outlying region to a meeting to allow the factions to present their opinions.
The Bishop was invited to attend or to send a representative.
The Council would render a decision on who would be allowed to continue to proclaim their views.
This meeting, known as the first Zürich Disputation, took place on 29 January 1523.
The meeting attracted a large crowd of approximately 600 participants.
The Bishop sent a delegation led by his Vicar General, Johan Faber.

Above: Johann Faber (1478 – 1541) epitaph, Vienna Cathedral
Zwingli summarised his position in the Schlussreden (Concluding Statements or the Sixty-seven Articles).
Fabri, who had not envisaged an academic disputation in the manner Zwingli had prepared for, was forbidden to discuss high theology before laymen, and simply insisted on the necessity of the ecclesiastical authority.
The decision of the Council was that Zwingli would be allowed to continue his preaching and that all other preachers should teach only in accordance with Scripture.
In September 1523, Leo Jud, Zwingli’s closest friend and colleague and pastor of St. Peterskirche (St. Peter’s Church), publicly called for the removal of statues of saints and other icons.
This led to demonstrations and iconoclastic (icon destruction) activities.

The City Council decided to work out the matter of images in a second disputation.
The essence of the Mass and its sacrificial character was also included as a subject of discussion.
Supporters of the Mass claimed that the Eucharist was a true sacrifice, while Zwingli claimed that it was a commemorative meal.
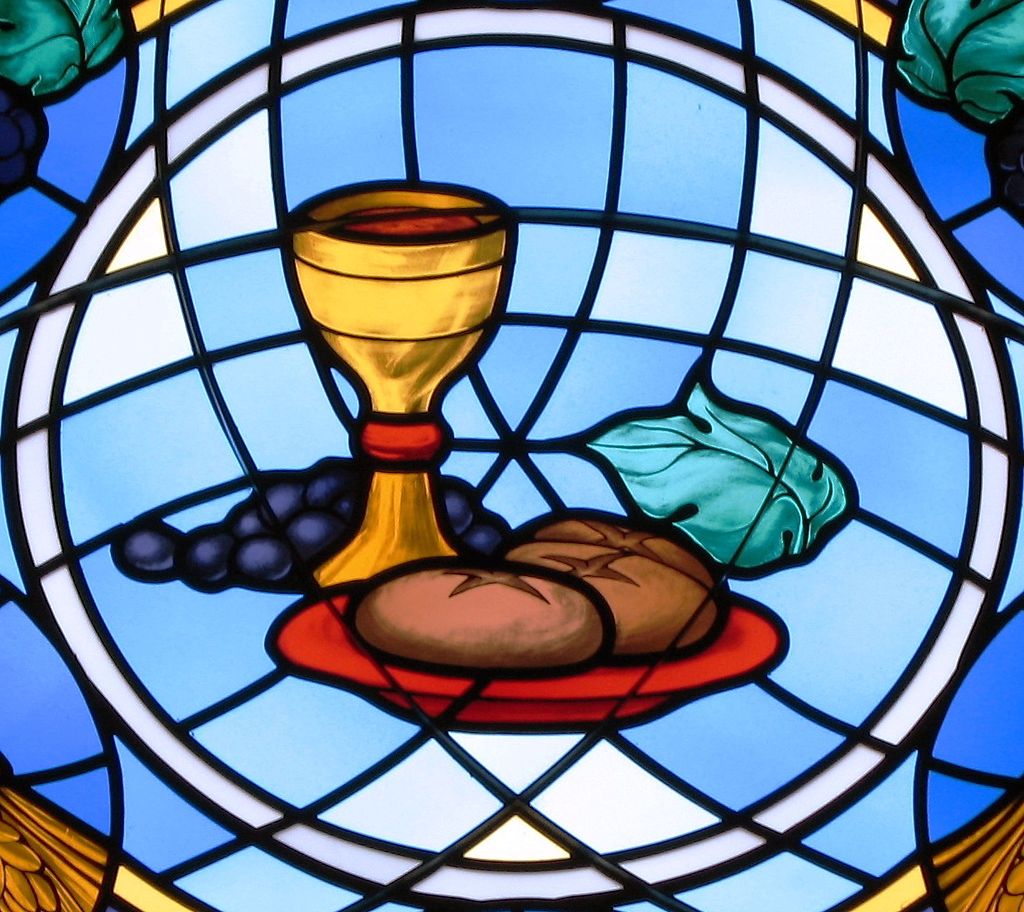

As in the first disputation, an invitation was sent out to the Zürich clergy and the Bishop of Konstanz.
This time, however, the lay people of Zürich, the Dioceses of Chur and Basel, the University of Basel, and the 12 members of the Confederation were also invited.

Above: Chur Cathedral
About 900 persons attended this meeting, but neither the bishop nor the Confederation sent representatives.
This Second Disputation started on 26 October 1523 and lasted two days.
Zwingli again took the lead in the disputation.
His opponent was the aforementioned canon, Konrad Hofmann, who had initially supported Zwingli’s election.
Also taking part was a group of young men demanding a much faster pace of reformation, who among other things pleaded for replacing infant baptism with adult baptism.

This group was led by Konrad Grebel, one of the initiators of the Anabaptist movement.

Above: Commemorative plaque for Konrad Grebel (1498 – 1526), Neumarkt, Zürich
During the first three days of dispute, although the controversy of images and the mass were discussed, the arguments led to the question of whether the City Council or the ecclesiastical government had the authority to decide on these issues.
At this point, Konrad Schmid, a priest from Aargau and follower of Zwingli, made a pragmatic suggestion.
As images were not yet considered to be valueless by everyone, he suggested that pastors preach on this subject under threat of punishment.
He believed the opinions of the people would gradually change and the voluntary removal of images would follow.
Hence, Schmid rejected the radicals and their iconoclasm, but supported Zwingli’s position.
In November the Council passed ordinances in support of Schmid’s motion.
Zwingli wrote a booklet on the evangelical duties of a minister, Kurze christliche Einleitung (short Christian introduction) and the Council sent it out to the clergy and the members of the Confederation.

Above: Coat of arms of Zürich
In December 1523, the council set the deadline of Pentecost 1524 for a solution to the elimination of the Mass and icons.

(Pentecost is the 50th day (the 7th Sunday) after Easter Sunday, commemorates the descent of the Holy Spirit upon the Apostles (disciples of Christ) and other followers of Jesus while they were in Jerusalem celebrating the Feast of Weeks, as described in Acts 2: 1 -31).

Zwingli gave a formal opinion in Vorschlag wegen der Bilder und der Messe (Proposal Concerning Images and the Mass).
He did not urge an immediate general abolition.
The Council decided on the orderly removal of images within Zürich, but rural congregations were granted the right to remove them based on majority vote.
The decision on the Mass was postponed.

Evidence of the effect of the Reformation was seen in early 1524.
Candlemas (2 February) was not celebrated, processions of robed clergy ceased, worshippers did not go with palms or relics on Palm Sunday to the Lindenhof, and triptychs (works of arts – usually panel paintings that are divided into three sections, or three carved panels that are hinged together and can be folded shut or displayed open) remained covered and closed after Lent.

Above: Blessing of candles on Candlemas

Above: Jesus’ entry into Jerusalem, frescoes by Pietro Lorenzetti, Assisi, Italy
(Palm Sunday is a Christian moveable feast that falls on the Sunday before Easter.
The feast commemorates Jesus’ triumphial entry into Jerusalem, an event mentioned in each of the four canonical Gospels.
Palm Sunday marks the first day of Holy Week, the last week of the Christian solemn season of Lent that precedes the arrival of Easter.)

Above: Palm Sunday procession, Moscow, with Tsar Alexei Michaelovich

Above: Lindenhof, Zürich

Above: Triptych, The Garden of Earthly Delights, Hieronymus Bosch, 1910
Opposition to the changes came from Konrad Hofmann and his followers, but the Council decided in favour of keeping the government mandates.
When Hofmann left the city, opposition from pastors hostile to the Reformation broke down.
The Bishop of Konstanz tried to intervene in defending the mass and the veneration of images.
Zwingli wrote an official response for the council and the result was the severance of all ties between the City and the Diocese.
Although the Council had hesitated in abolishing the Mass, the decrease in the exercise of traditional piety allowed pastors to be unofficially released from the requirement of celebrating Mass.
As individual pastors altered their practices as each saw fit, Zwingli was prompted to address this disorganised situation by designing a communion liturgy in the German language.
This was published in Aktion oder Brauch des Nachtmahls (Act or Custom of Communion).
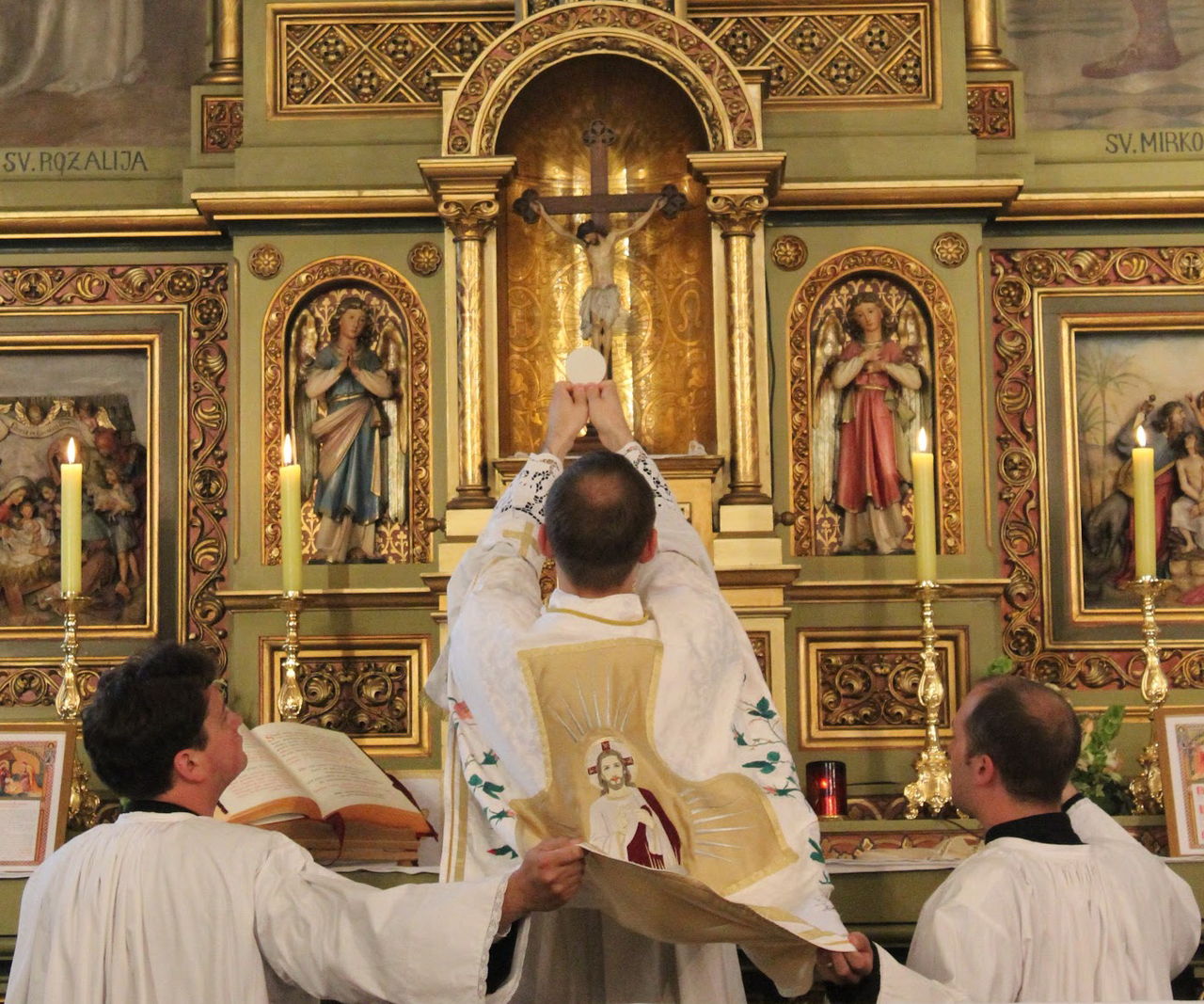

Shortly before Easter, Zwingli and his closest associates requested the Council to cancel the Mass and to introduce the new public order of worship.
On Maundy Thursday, 13 April 1525, Zwingli celebrated communion under his new liturgy.
Wooden cups and plates were used to avoid any outward displays of formality.
The congregation sat at set tables to emphasise the meal aspect of the sacrament.
The sermon was the focal point of the service and there was no organ music or singing.
The importance of the sermon in the worship service was underlined by Zwingli’s proposal to limit the celebration of communion to four times a year.

Above: Statue of Zwingli in front of the Wasserkirche (water church) in Zürich
(Maundy Thursday is the Christian holy day falling on the Thursday before Easter.
It commemorates the Washing of the Feet (Maundy) and the Last Supper of Jesus Christ with the Apostles, as described in the canonical gospels.)

For some time Zwingli had accused mendicant orders of hypocrisy and demanded their abolition in order to support the truly poor.
He suggested that monasteries be changed into hospitals and welfare institutions and incorporate their wealth into a welfare fund.
This was done by reorganising the foundations of the Grossmünster and Fraumünster (women’s cathedral) and pensioning off remaining nuns and monks.
The Council secularised the church properties (Fraumünster handed over by Zwingli’s acquaintance Katharina von Zimmern) and established new welfare programs for the poor.

Above: Katharina von Zimmern plaque, Fraumünster, Zürich
Zwingli requested permission to establish a Latin school, the Prophezei (prophecy) or Carolinum, at the Grossmünster.
The Council agreed and the school was officially opened on 19 June 1525 with Zwingli and Jud as teachers.
It served to retrain and re-educate the clergy.

Above: Carolinum (left) / Grossmünster (right), Zürich
The Zürich Bible translation, traditionally attributed to Zwingli and printed by Christoph Froschauer, bears the mark of teamwork from the Prophecy school.
Scholars have not yet attempted to clarify Zwingli’s share of the work based on external and stylistic evidence.

Shortly after the Second Zürich Disputation, many in the radical wing of the Reformation became convinced that Zwingli was making too many concessions to the Zürich Council.
They rejected the role of civil government and demanded the immediate establishment of a congregation of the faithful.
Conrad Grebel, the leader of the radicals and the emerging Anabaptist movement, spoke disparagingly of Zwingli in private.
On 15 August 1524 the Council insisted on the obligation to baptise all newborn infants.
When Grebel joined the Anabaptist group in 1521, he and Felix Manz became friends.
They questioned the mass, the nature of church and state connections, and infant baptism.
Grebel, Manz and others made several attempts to plead their position.
Several parents refused to have their children baptized.
A public disputation was held with Zwingli on 17 January 1525.
The Council declared Zwingli the victor.
When talks were broken off, Zwingli published Wer Ursache gebe zu Aufruhr (Whoever Causes Unrest) clarifying the opposing points-of-view.
After the final rebuff by the city council on 18 January, in which they were ordered to desist from arguing and submit to the decision of the council, and have their children baptized within eight days, the brethren gathered at the home of Felix Manz and his mother on 21 January.
Conrad Grebel baptized George Blaurock, and Blaurock in turn baptized the others.
This made complete the break with Zwingli and the council, and formed the first church of the Radical Reformation.
The movement spread rapidly, and Manz was very active in it.
He used his language skills to translate his texts into the language of the people, and worked enthusiastically as an evangelist.
Manz was arrested on a number of occasions between 1525 and 1527.
While he was preaching with George Blaurock in the Grüningen region, they were taken by surprise, arrested and imprisoned in Zürich at the Wellenburg prison.

Above: Felix Manz (1498 – 1527)
Grebel and a third leader, George Blaurock, performed the first recorded Anabaptist adult baptisms.
On 2 February, the Council repeated the requirement on the baptism of all babies and some who failed to comply were arrested and fined, Manz and Blaurock among them.
Zwingli and Jud interviewed them and more debates were held before the Zürich council.
Meanwhile, the new teachings continued to spread to other parts of the Confederation as well as a number of Swabian (Württemburg) towns.
On 6 – 8 November, the last debate on the subject of baptism took place in the Grossmünster.
Grebel, Manz and Blaurock defended their cause before Zwingli, Jud, and other reformers.
There was no serious exchange of views as each side would not move from their positions and the debates degenerated into an uproar, each side shouting abuse at the other.
The Zürich Council decided that no compromise was possible.
On 7 March 1526, it released the notorious mandate that no one shall rebaptise another under the penalty of death by drowning.
Although Zwingli, technically, had nothing to do with the mandate, there is no indication that he disapproved.
Felix Manz, who had sworn to leave Zürich and not to baptise any more, had deliberately returned and continued the practice.
On 5 January 1527, Manz became the first casualty of the edict, and the first Swiss Anabaptist to be martyred at the hands of magesterial Protestants.
While Manz stated that he wished “to bring together those who were willing to accept Christ, obey the Word, and follow in His footsteps, to unite with these by baptism, and to purchase the rest in their present conviction“, Zwingli and the council accused him of obstinately refusing “to recede from his error and caprice“.
At 3:00 p.m., as he was led from the Wellenburg to a boat, he praised God and preached to the people.
A Reformed minister went along, seeking to silence him, and hoping to give him an opportunity to recant.
Manz’s brother and mother encouraged him to stand firm and suffer for Jesus’ sake.
Manz was taken by boat onto the River Limmat
His hands were bound and pulled behind his knees and a pole was placed between them.
He was executed by drowning in Lake Zürich on the Limmat River.
His alleged last words were:
“Into thy hands, O God, I commend my spirit.”
His property was confiscated by the government of Zürich, and he was buried in St. Jakobs Cemetery.
Manz left written testimony of his faith, an eighteen-stanza hymn, and was apparently the author of Protestation und Schutzschrift (a defense of Anabaptism presented to the Zürich Council).

Above: Felix Manz’s Protestation und Schutzschrift (protest and written defence)
He was the first Anabaptist martyr.
Three more were to follow, after which all others either fled or were expelled from Zürich.

Above: Memorial plate on the river wall opposite number 43 Schipfe, Zürich, in remembrance of Manz and other Anabaptists executed in the early 16th century by the Zürich city government
On 8 April 1524, five cantons, Luzern, Uri, Schwyz, Unterwalden and Zug, formed an alliance, die fünf Orte (the Five States) to defend themselves from Zwingli’s Reformation.
They contacted the opponents of Martin Luther, including Johann Eck who had debated Luther in the Leipzig Disputation of 1519.
Eck offered to dispute Zwingli and he accepted.

Above: Johannes Maier von Eck (1486 – 1543)
However, they could not agree on the selection of the judging authority, the location of the debate, and the use of the Swiss Diet as a court.
Because of the disagreements, Zwingli decided to boycott the disputation.
On 19 May 1526, all the cantons sent delegates to Baden.
Although Zürich’s representatives were present, they did not participate in the sessions.

Above: Baden, Switzerland
Eck led the Catholic party while the reformers were represented by Johannes Oecolampadius of Basel, a theologian from Württemberg who had carried on an extensive and friendly correspondence with Zwingli.

Above: Johannes Oecolampadius (1482 – 1531)
While the debate proceeded, Zwingli was kept informed of the proceedings and printed pamphlets giving his opinions.
It was of little use as the Diet decided against Zwingli.
He was to be banned and his writings were no longer to be distributed.
Of the 13 Confederation members, Glarus, Solothurn, Fribourg/Freiburg, and Appenzell, as well as the Five States voted against Zwingli.
Bern, Basel, Schaffhausen and Zürich supported him.

Above: Map of the thirteen cantons of the Swiss confederacy in 1530 (green) with their separate subject territories (light green), condominiums (grey) and associates (brown)
The Baden Disputation exposed a deep rift in the Confederation on matters of religion.
The Reformation was now emerging in other states.

Above: Baden, Switzerland
The city of St. Gallen, an affiliated state to the Confederation, was led by a reformed mayor, Joachim Vadian, and the city abolished the mass in 1527, just two years after Zürich.

Above: Abbey Church, St. Gallen

Above: Joachim Vadian (né Joachim von Watt) (1484 – 1551)
In Basel, although Zwingli had a close relationship with Oecolampadius, the government did not officially sanction any reformatory changes until 1 April 1529 when the Mass was prohibited.

Above: Basel, Switzerland
Schaffhausen, which had closely followed Zürich’s example, formally adopted the Reformation in September 1529.

Above: Schaffhausen, Switzerland
In the case of Bern, Berchtold Haller, the priest at St. Vincent Münster, and Niklaus Manuel, the poet, painter and politician, had campaigned for the reformed cause.
But it was only after another Disputation that Bern counted itself as a canton of the Reformation.
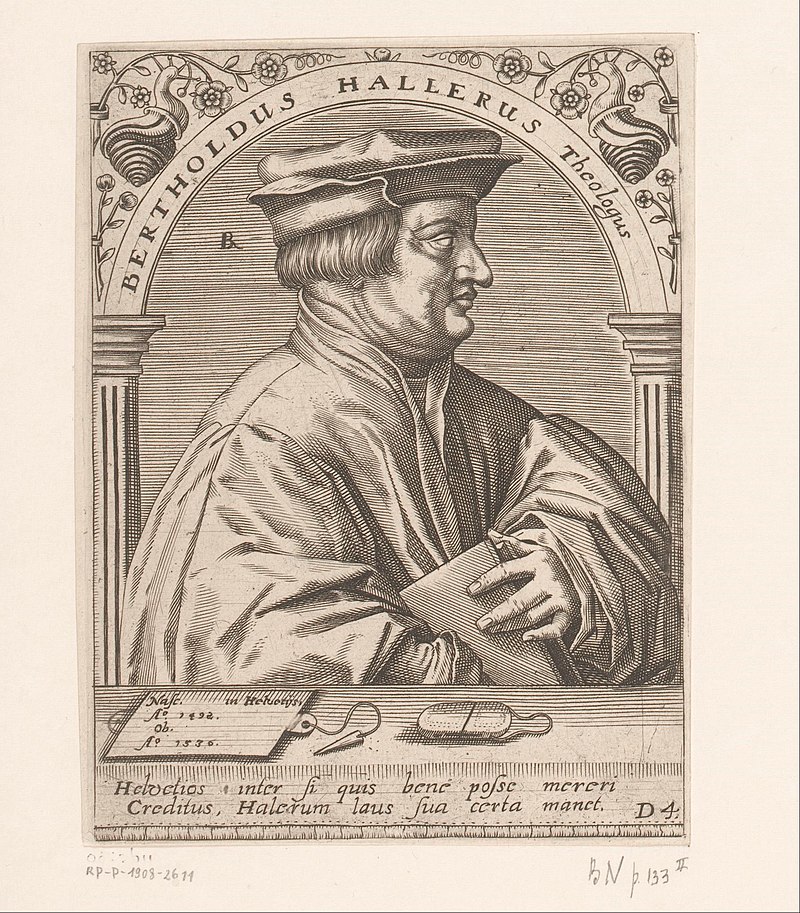

Above: Berchtold Haller (1492 – 1536)
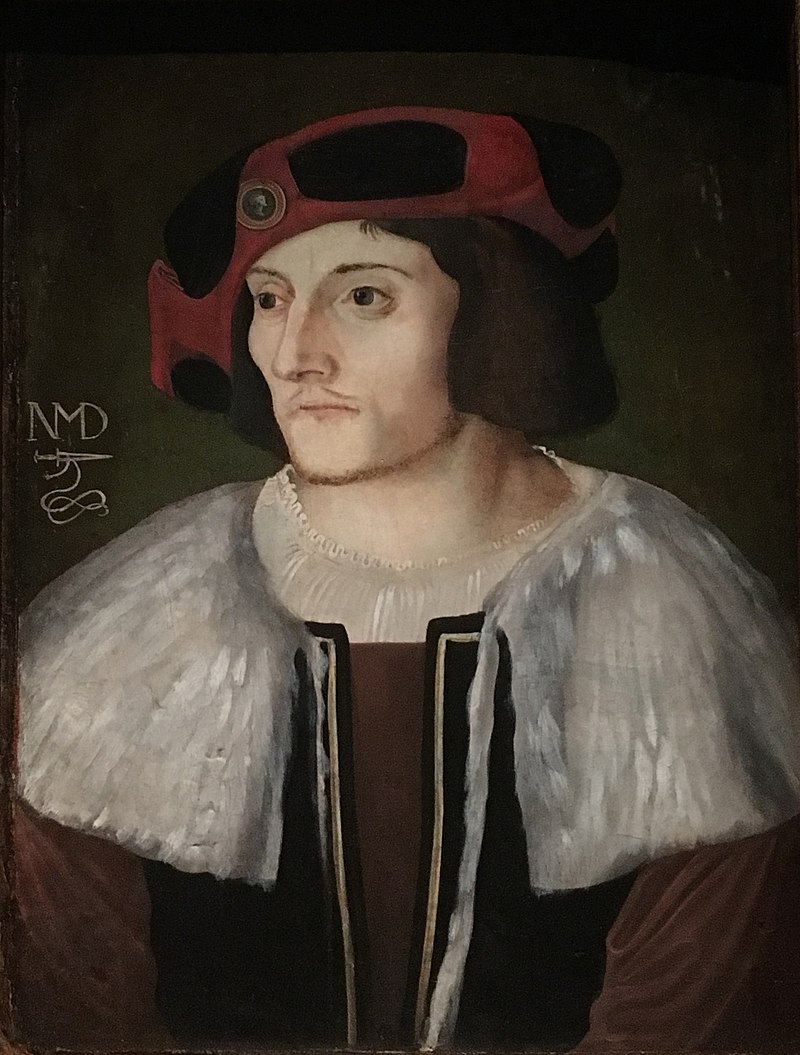

Above: Niklaus Manuel (1484 – 1530)
450 persons participated, including pastors from Bern and other cantons, as well as theologians from outside the Confederation, such as:
- Martin Bucer (1491 – 1551) from Strasbourg

- Wolfgang Capito (1478 – 1541) from Strasbourg

- Ambrosius Blarer (1492 – 1564) from Konstanz

- Andreas Althamer (1500 – 1539) from Nuremberg

Eck and Fabri refused to attend and the Catholic cantons did not send representatives.
The meeting started on 6 January 1528 and lasted nearly three weeks.
Zwingli assumed the main burden of defending the Reformation and he preached twice in the Münster.
On 7 February 1528, the Council decreed that the Reformation be established in Bern.

Above: Bern, Switzerland
In the years following his recovery from the plague, Zwingli’s opponents remained in the minority.
When a vacancy occurred among the canons of the Grossmünster, Zwingli was elected to fulfill that vacancy on 29 April 1521.
In becoming a canon, he became a full citizen of Zürich.
He also retained his post as the people’s priest of the Grossmünster.
Historians have debated whether or not he turned Zürich into a theocracy.

Above: Images of Zürich
Even before the Bern Disputation, Zwingli was canvassing for an alliance of reformed cities.
Once Bern officially accepted the Reformation, a new alliance, das Christliche Burgrecht (the Christian Civic Union) was created.
The first meetings were held in Bern between representatives of Bern, Konstanz and Zürich on 5 – 6 January 1528.
Other cities, including Basel, Biel / Bienne, Mülhausen, Schaffhausen and St Gallen, eventually joined the alliance.
The Five (Catholic) States felt encircled and isolated, so they searched for outside allies.
After two months of negotiations, the Five States formed die Christliche Vereinigung (the Christian Alliance) with Ferdinand of Austria on 22 April 1529.

Above: Ferdinand I of Austria, Holy Roman Emperor (1503 – 1564)
Soon after the Austrian treaty was signed, a reformed preacher, Jacob Kaiser, was captured in Uznach and executed in Schwyz.

Above: Schwyz, Switzerland
This triggered a strong reaction from Zwingli.
Zwingli drafted Ratschlag über den Krieg (Advice About the War) for the government.
Zwingli outlined justifications for an attack on the Catholic states and other measures to be taken.
Before Zürich could implement his plans, a delegation from Bern, that included Niklaus Manuel, arrived in Zürich.
The delegation called on Zürich to settle the matter peacefully.
Manuel added that an attack would expose Bern to further dangers as Catholic Valais and the Duchy of Savoy bordered its southern flank.
He then noted:
“You cannot really bring faith by means of spears and halberds.“

Zürich, however, decided that it would act alone, knowing that Bern would be obliged to acquiesce.
War was declared on 8 June 1529.
Zürich was able to raise an army of 30,000 men.
The Five States were abandoned by Austria and could raise only 9,000 men.
The two forces met near Kappel, but war was averted due to the intervention of Hans Aebli, a relative of Zwingli, who pleaded for an armistice.
Zwingli was obliged to state the terms of the armistice.
He demanded the dissolution of the Christian Alliance, unhindered preaching by reformers in the Catholic states, prohibition of the pension system, payment of war reparations, and compensation to the children of Jacob Kaiser.
Manuel was involved in the negotiations.
Bern was not prepared to insist on the unhindered preaching or the prohibition of the pension system.
Zürich and Bern could not agree and the Five (Catholic) States pledged only to dissolve their alliance with Austria.
This was a bitter disappointment for Zwingli and it marked his decline in political influence.
Der erste Landfriede (the first Land Peace) of Kappel ended the war, a war without bloodshed or battle, on 24 June.
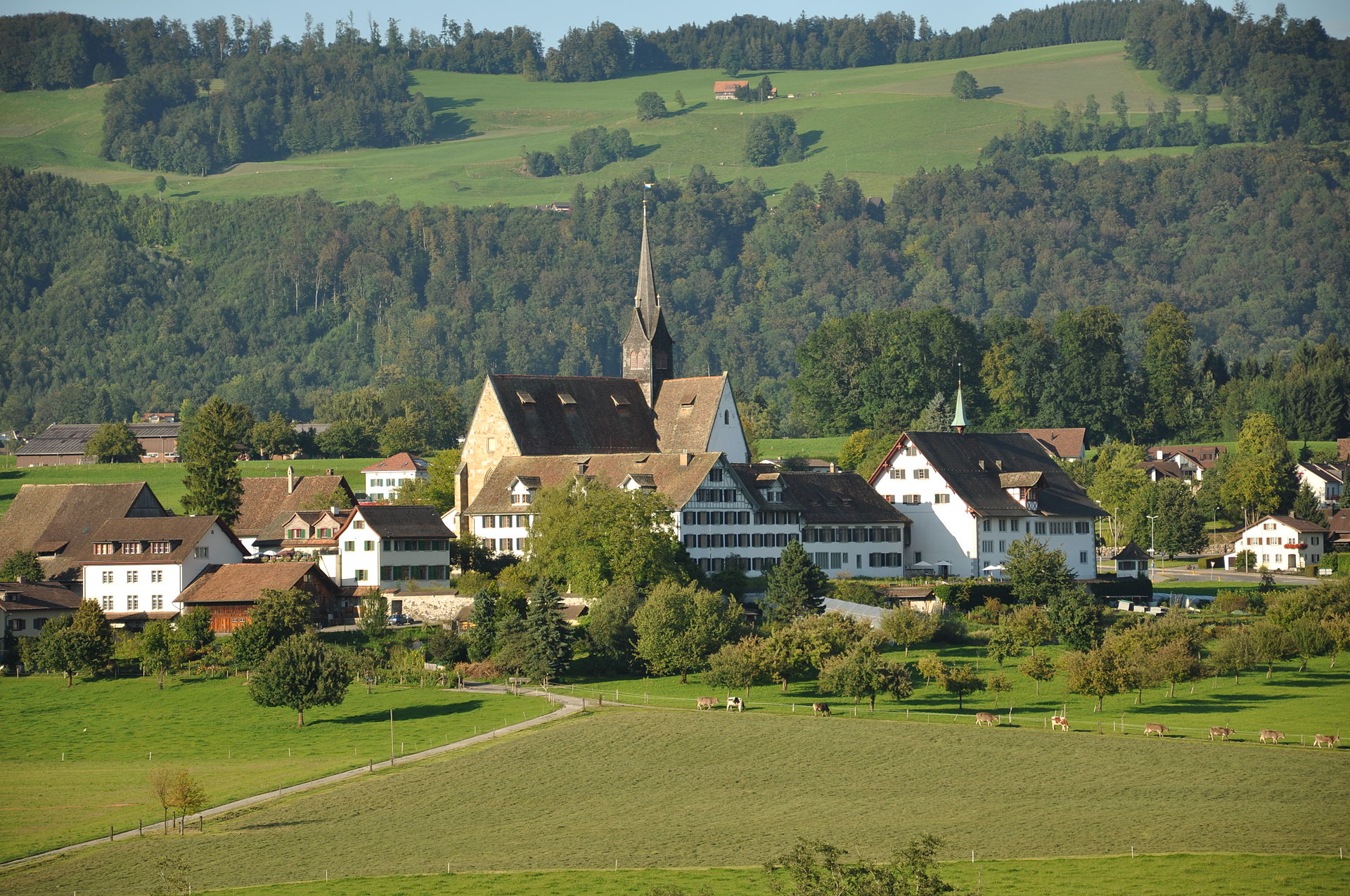

Above: Kappel am Albis
While Zwingli carried on the political work of the Swiss Reformation, he developed his theological views with his colleagues.
The famous disagreement between Luther and Zwingli on the interpretation of the Eucharist originated when Andreas Karlstadt, Luther’s former colleague from Wittenberg, published three pamphlets on the Lord’s Supper in which Karlstadt rejected the idea of a real presence in the elements.

Above: Andreas Rudolph Bodenstein von Karlstadt (1486 – 1541)

These pamphlets, published in Basel in 1524, received the approval of Oecolampadius and Zwingli.
Luther rejected Karlstadt’s arguments and considered Zwingli primarily to be a partisan of Karlstadt.
Zwingli began to express his thoughts on the Eucharist in several publications including de Eucharistia (On the Eucharist).
Understanding that Christ had ascended to Heaven and was sitting at the Father’s right hand, Zwingli criticized the idea that Christ’s humanity could be in two places at once.
Unlike his divinity, Christ’s human body was not omnipresent and so could not be in Heaven and at the same time be present in the elements.

Timothy George, evangelical author, editor of Christianity Today and professor of Historical Theology at Beeson Divinity School at Samford University, has firmly refuted a long-standing misreading of Zwingli that erroneously claimed the Reformer denied all notions of real presence and believed in a memorial view of the Last Supper, where it was purely symbolic.

By spring 1527, Luther reacted strongly to Zwingli’s views in the treatise Dass Diese Worte Christi “Das ist mein Leib etc.” noch fest stehen wider die Schwarmgeister (That These Words of Christ “This is My Body etc.” Still Stand Firm Against the Fanatics).
The controversy continued until 1528 when efforts to build bridges between the Lutheran and the Zwinglian views began.
Martin Bucer tried to mediate while Philip of Hesse, who wanted to form a political coalition of all Protestant forces, invited the two parties to Marburg to discuss their differences.

Above: Philip I, Landgrave of Hesse (1504 – 1567), nicknamed der Großmütige (“the magnanimous“)
This event became known as the Marburg Colloquy.
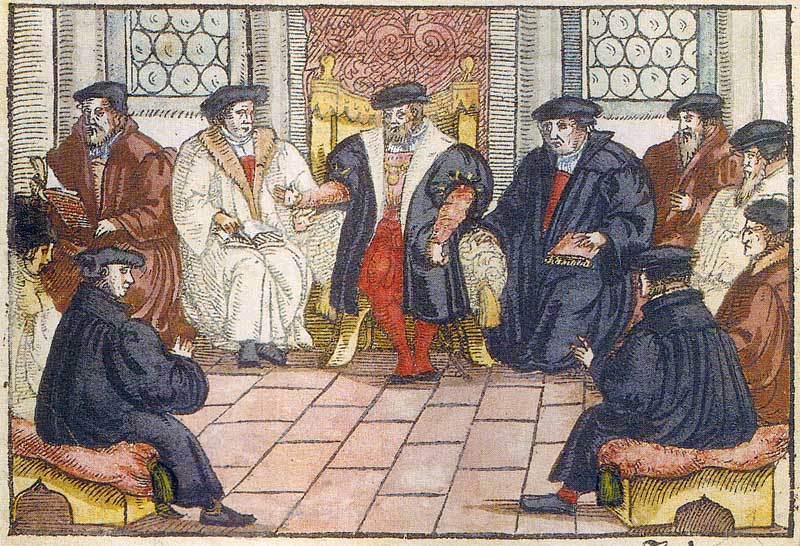
Zwingli accepted Philip’s invitation fully believing that he would be able to convince Luther.
In contrast, Luther did not expect anything to come out of the meeting and had to be urged by Philip to attend.
Zwingli, accompanied by Oecolampadius, arrived on 28 September 1529, with Luther and Philip Melanthchon arriving shortly thereafter.

Above: Philipp Melanchthon (né Philipp Schwartzerdt) (1497 – 1560)
Other theologians also participated including Martin Bucer, Andreas Osiander, Johannes Brenz and Justus Jonas.

Above: Andreas Osiander (1498 – 1552)

Above: Johann Brenz (1499 – 1570)

Above: Justus Jonas (1493 – 1555)
The debates were held from 1–4 October and the results were published in the fifteen Marburg Articles.
The participants were able to agree on 14 of the articles, but the 15th article established the differences in their views on the presence of Christ in the Eucharist.

Professor George summarized the incompatible views:
“On this issue, they parted without having reached an agreement.
Both Luther and Zwingli agreed that the bread in the Last Supper was a sign.
For Luther, however, that which the bread signified, namely the body of Christ, was present “in, with, and under” the sign itself.
For Zwingli, though, sign and thing signified were separated by a distance — the width between Heaven and Earth.“
“Luther claimed that the body of Christ was not eaten in a gross, material way, but rather in some mysterious way, which is beyond human understanding.
Yet, Zwingli replied, if the words were taken in their literal sense, the body had to be eaten in the most grossly material way.
“For this is the meaning they carry:
This bread is that body of mine which is given for you.
It was given for us in grossly material form, subject to wounds, blows and death.
As such, therefore, it must be the material of the Last Supper.”
Indeed, to press the literal meaning of the text even farther, it follows that Christ would have again to suffer pain, as his body was broken again — this time by the teeth of communicants.
Even more absurdly, Christ’s body would have to be swallowed, digested, even eliminated through the bowels!
Such thoughts were repulsive to Zwingli.
They smacked of cannibalism on the one hand and of the pagan mystery religions on the other.
The main issue for Zwingli, however, was not the irrationality or exegetical fallacy of Luther’s views.
It was rather that Luther put “the chief point of salvation in physically eating the body of Christ”, for he connected it with the forgiveness of sins.
The same motive that had moved Zwingli so strongly to oppose images, the invocation of saints, and baptismal regeneration was present also in the struggle over the Last Supper: the fear of idolatry.
Salvation was by Christ alone, through faith alone, not through faith and bread.
The object of faith was that which is not seen (Hebrews 11:1) and which therefore cannot be eaten except, again, in a nonliteral, figurative sense.
“Credere est edere,” said Zwingli.
(“To believe is to eat.”)
To eat the body and to drink the blood of Christ in the Last Supper, then, simply meant to have the body and blood of Christ present in the mind.”

The failure to find agreement resulted in strong emotions on both sides.
When the two sides departed, Zwingli cried out in tears:
“There are no people on Earth with whom I would rather be at one than the Lutheran Wittenbergers.”
Because of the differences, Luther initially refused to acknowledge Zwingli and his followers as Christians.

Above: Huldrych Zwingli
With the failure of the Marburg Colloquy and the split of the Confederation, Zwingli set his goal on an alliance with Philip of Hesse.
He kept up a lively correspondence with Philip.
Bern refused to participate, but after a long process, Zürich, Basel and Strasbourg signed a mutual defence treaty with Philip in November 1530.
Zwingli also personally negotiated with France’s diplomatic representative, but the two sides were too far apart.
France wanted to maintain good relations with the Five States.
Approaches to Venice and Milan also failed.
As Zwingli was working on establishing these political alliances, Charles V, the Holy Roman Emperor, invited Protestants to the Augsburg Diet to present their views so that he could make a verdict on the issue of faith.

Above: Emperor Charles V (1500 – 1558)
The Lutherans presented the Augsburg Confession.

Above: Saxon chancellor Christian Beyer proclaiming the Augsburg Confession in the presence of Emperor Charles V, 1530
Under the leadership of Martin Bucer, the cities of Strasbourg, Konstanz, Memmingen and Lindau produced the Tetrapolitan (of the Four Cities) Confession.
This document attempted to take a middle position between the Lutherans and Zwinglians.

Above: Nôtre Dame Cathedral, Strasbourg

Above. Konstanz Cathedral

Above: Rathaus (city hall), Memmingen
Due to its proximity to the Allgäu region, Memmingen is often called the Gateway to the Allgäu (Tor zum Allgäu).
The town motto is Memmingen – Stadt mit Perspektiven (“Memmingen – a town with perspectives“).
In recent times it has been frequently referred to as Memmingen – Stadt der Menschenrechte (Memmingen – the town of human rights).
This alludes to the Twelve Articles, considered to be the first written set of human rights in Europe, which were penned in Memmingen in 1525.

Above: The Twelve Articles

Above: Town hall, Lindau
It was too late for the Burgrecht cities to produce a confession of their own.
Zwingli then produced his own private confession, Fidei ratio (Account of Faith) in which he explained his faith in 12 articles conforming to the articles of the Apostles’ Creed.

Above: The rubric above this 13th-century illuminated manuscript translates “twelve articles of faith set out by twelve apostles“.
The tone was strongly anti-Catholic as well as anti-Lutheran.
The Lutherans did not react officially, but criticised it privately.
Zwingli’s and Luther’s old opponent, Johann Eck, counter-attacked with a publication, Refutation of the Articles Zwingli Submitted to the Emperor.
When Philip of Hesse formed the Schmalkaldic League at the end of 1530, the four cities of the Tetrapolitan Confession joined on the basis of a Lutheran interpretation of that confession.
Given the flexibility of the League’s entrance requirements, Zürich, Basel, and Bern also considered joining.

Above: Schmalkaldic League military treaty, extended in 1536
However, Zwingli could not reconcile the Tetrapolitan Confession with his own beliefs and wrote a harsh refusal to Bucer and Capito.
This offended Philip to the point where relations with the League were severed.
The Burgrecht cities now had no external allies to help deal with internal Confederation religious conflicts.
Above: Philip of Hesse
The peace treaty of the First Kappel War did not define the right of unhindered preaching in the Catholic states.
Zwingli interpreted this to mean that preaching should be permitted, but the Five States suppressed any attempts to reform.

Above: Huldrych Zwingli
The Burgrecht cities considered different means of applying pressure to the Five States.
Basel and Schaffhausen preferred quiet diplomacy while Zürich wanted armed conflict.
Zwingli and Jud unequivocally advocated an attack on the Five States.
Bern took a middle position which eventually prevailed.

Above: Coat of arms of Basel

Above: Coat of arms of Schaffhausen
In May 1531, Zürich reluctantly agreed to impose a food blockade.
It failed to have any effect and in October, Bern decided to withdraw the blockade.
Zürich urged its continuation and the Burgrecht cities began to quarrel among themselves.

Above: Coat of arms of Bern
On 9 October 1531, in a surprise move, the Five States declared war on Zürich….
(To be continued…..)

Sources: Wikipedia / Google / Duncan J.D. Smith, Only in Zürich / Yvonne and Marcel Steiner, Zwingli-Wege







































































![en:slccs [Bibliothèque numérique du CF]](https://www.cactuspro.com/biblio/_media/slccsthumb.jpg)